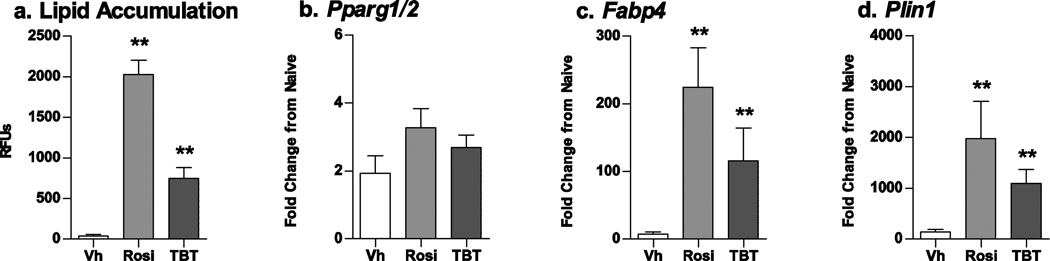
Figure 2. Known modulators of adipogenesis increase lipid accumulation and expression of adipogenic genes in mouse BM-MSCs.
Primary bone marrow cultures were established from male C57BL/6J mice and treated with vehicle (Vh, DMSO), rosiglitazone (Rosi, 100 nM) or TBT (100 nM) in the presence of osteoinductive media for 7 (gene expression) or 11 days (lipid accumulation). (A) Lipid accumulation was quantified by Nile Red staining. (B–D) mRNA expression was quantified by RT-qPCR. Data are presented as means ± SE (n = 4–8 independent bone marrow preparations). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared to Vh-treated cultures (ANOVA, Dunnett’s). Vehicle-treated cells showed increases in expression of adipocyte-related genes relative to undifferentiated cells (1.9-fold for PPARγ, 7.7-fold for Fabp4, and 144.4-fold for Plin1).