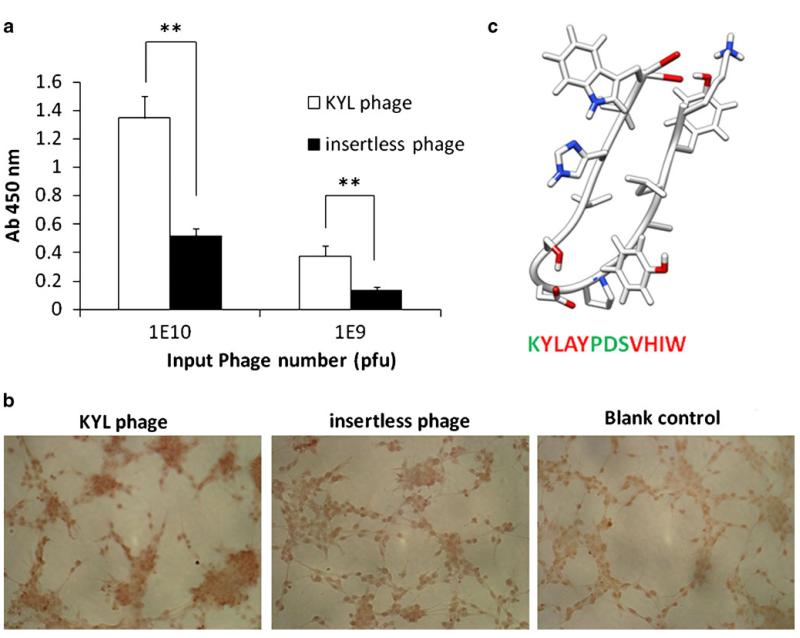
Fig. 2.
Determination of the binding of KYL phage on LNCaP cells by cell phage ELISA (a) and immunostaining (b). (a) LNCaP cells (50,000 cells per well) were cultured in 96-well plates were fixed with cold methanol-acetone (1:1, v/v). The KYL phage and insertless phage (109 and 1010 pfu) were incubated with the cells for 1 h, and the bound phages were determined by cell phage ELISA. Results are represented as the mean±SD (n=3).*p<0.05, **p<0.01. (b) LNCaP cells cultured on Lab-TEK® 8-well chamber slides were fixed and incubated with ~1010 pfu phages at room temperature for 1 h. The cells were incubated with HRP-conjugated anti-M13 monoclonal antibody at room temperature for 1 h and then visualized using the DAB substrate. (c) Computer-generated model structure of the KYL peptide. The KYL peptide sequence was analyzed using mobile (http://mobyle.rpbs.univ-paris-diderot.fr/cgi-bin/portal.py?form=PEP-FOLD#). The structure was obtained by UCSF chimera molecular modeling system using the mobile-generated PDB file. Green color indicates hydrophilic residues, and red color indicates hydrophobic residues.