FIG 2.
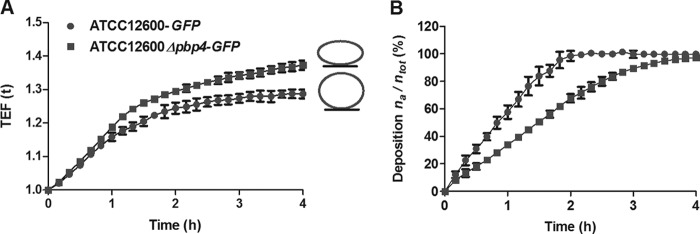
Effects of pbp4 deletion on cell wall deformation. (A) Cell wall deformation of S. aureus ATCC 12600-GFP and S. aureus ATCC 12600 Δpbp4-GFP upon adhesion to SS, as measured using surface-enhanced fluorescence. As an adhering bacterium deforms, its fluorescent intracellular content gets closer to the reflecting metal surface, yielding a surface-enhanced fluorescence that increases with increasing deformation. Each point represents the average ± standard error of the mean from three individual experiments. All differences between S. aureus ATCC 12600 and S. aureus ATCC 12600 Δpbp4 were statistically significant (P < 0.05). (B) The number of adhering S. aureus ATCC 12600-GFP and S. aureus ATCC 12600 Δpbp4-GFP bacteria on SS surfaces as a function of sedimentation time, expressed as the percentage of bacteria adhering (na) with respect to the total number of bacteria (ntot) in the suspension volume above the substratum surface. Each point represents the average ± standard error of the mean from three individual experiments. All differences between S. aureus ATCC 12600 and S. aureus ATCC 12600 Δpbp4 were statistically significant (P < 0.05).
