Figure 1.
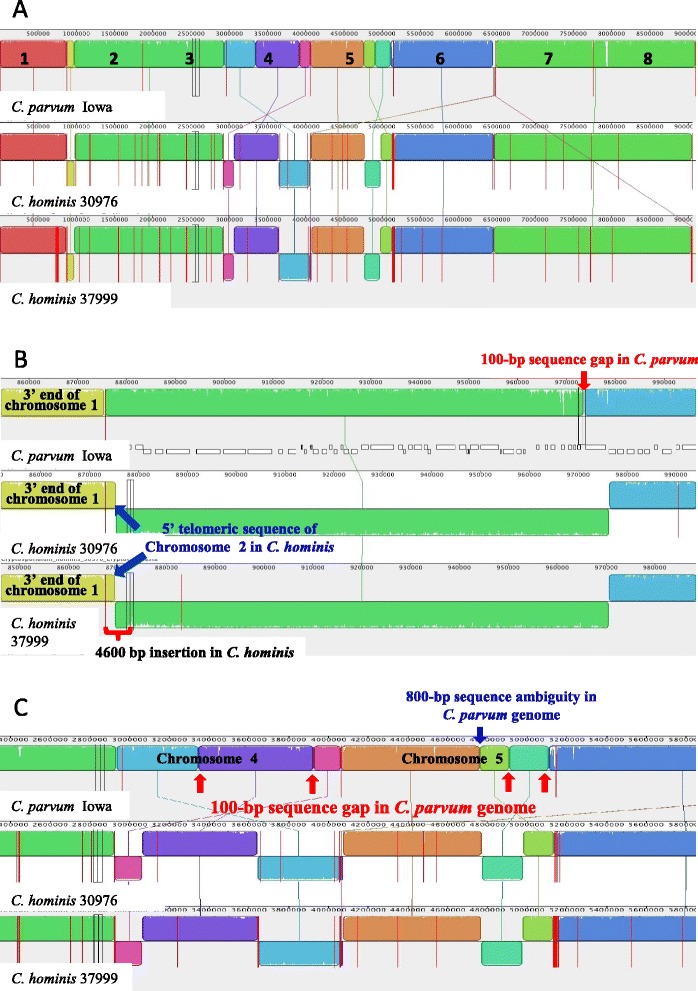
Structural organization of two Illumina-sequenced genomes of Cryptosporidium hominis comparing to eight chromosomes (numbered and separated by vertical red lines) of published Cryptosporidium parvum genome. The color blocks (known as Locally Collinear Blocks) are conserved segments of sequences internally free from genome rearrangements, whereas the inverted white peaks within each block are sequence divergence between the reference C. parvum (IOWA) genome and C. hominis genome under analysis. A. Coverage of two C. hominis genomes showing possible sequence rearrangements in chromosomes 2, 4, 5 and 6. Assembled contigs are bordered by vertical red lines. For specimens 30976, only Cryptosporidium contigs were used in mapping. B. Possible sequence rearrangements at the 5′ end of chromosome 2. C. Possible sequence rearrangements in chromosomes 4 and 5.
