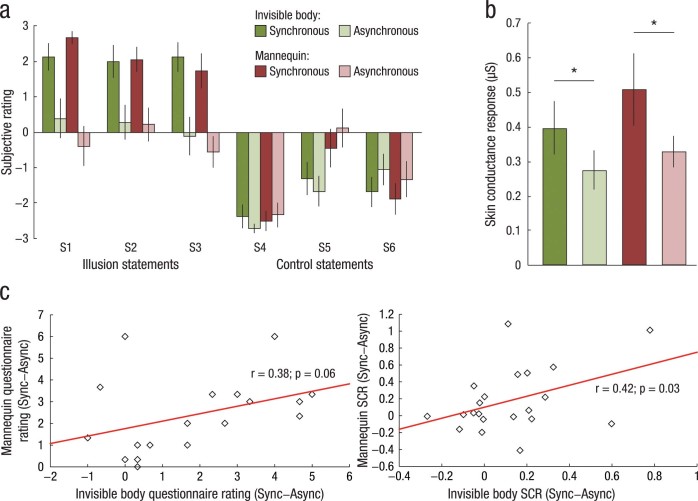
Figure 3. Results of Experiments 2a and 2b.
(a) The results of Experiment 2a show that strength of the invisible body illusion was equal to that of the mannequin illusion (the three-way interaction of body type × visuo-tactile temporal congruence × statement type was non-significant). (b) The SCR results of Experiment 2b show a significant main effect of visuo-tactile temporal congruence and a non-significant interaction of body type × visuo-tactile temporal congruence, corroborating the conclusion that the invisible body and mannequin illusions are of similar strengths. (c) There was a positive correlation between the magnitudes of the invisible body and mannequin illusions in terms of subjective ratings (left graph) and threat-evoked SCRs (right graph). These results imply that the elicitation of the illusions is dependent on analogous neural processes. *P < 0.05.