Figure 8.
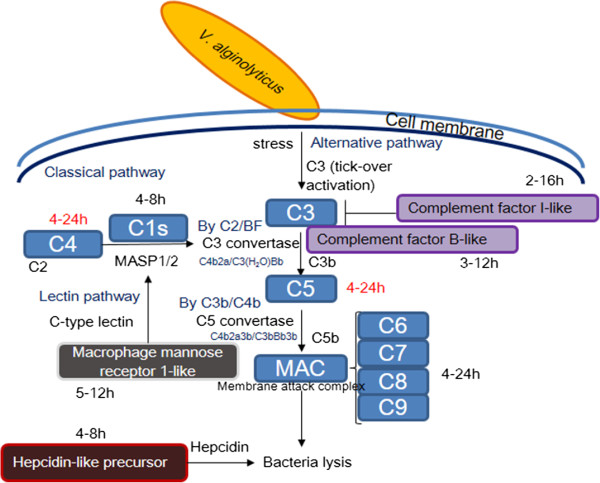
Predicted model of the immune response of Epinephelus coioides larvae to V. alginolyticus infection. The times (in h) besides each gene indicate the time post-V. alginolyticus infection at which its expression is significantly increased (red font indicates uncertainty). The classical pathway involves (i) cleavage of C4 to C3 convertase by C1s, (ii) cleavage of C3 to C3b by C3 convertase, (iii) combination of C3b with C5, (iv) cleavage of the resulting complex to C5b by C5 convertase, and (v) formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC) and lysis of V. alginolyticus. The lectin pathway involves C-type lectin-mediated cleavage of C4 and C2 by MASP1/2, and subsequent cleavage of C3 by C3 convertase. The alternative pathway involves cleavage of C3 by factor B; like the classical pathway, factor I acts as an inhibitor in the alternative pathway. Hepcidin may directly kill the bacterium by disrupting its membrane.
