FIGURE 2.
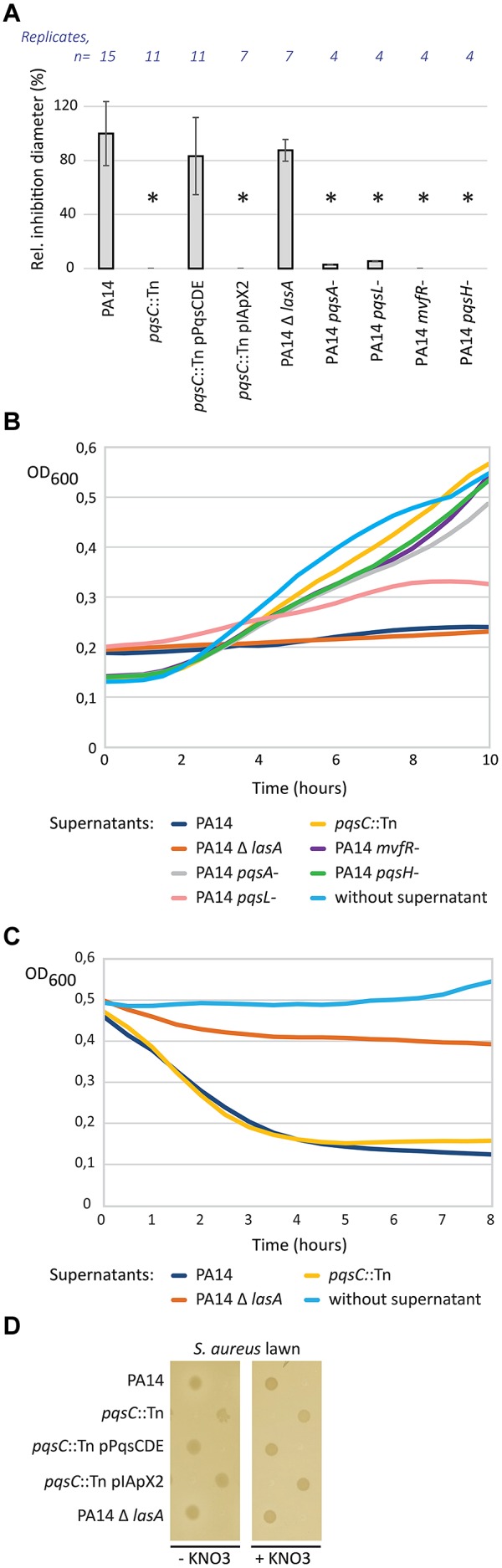
Role of the pqs pathway of P. aeruginosa in direct competition with S. aureus. (A) Effect of pqsC disruption on the inhibition of S. aureus growth. Spots of P. aeruginosa cultures were deposited on LB agar plates seeded with a lawn of S. aureus strain COL. Inhibition zone diameters were measured, normalized against the diameter of the corresponding spots and expressed as a percentage against the wild-type PA14 values. Error bars are standard deviations calculated on at least four replicates. Statistical significance was determined by using a t-test with unequal variances (∗p < 0.01). (B) Inhibition activity of P. aeruginosa supernatants on S. aureus growth. Supernatants of P. aeruginosa overnight cultures were incorporated on S. aureus cells. S. aureus growth (OD600) was monitored during 10 h at 37°C in presence to these supernatants. (C) Lytic activity of P. aeruginosa supernatants on inactivated S. aureus cells. Supernatants of P. aeruginosa overnight cultures were incorporated on heat-inactivated S. aureus cells. OD600 was monitored during 8 h at 37°C in presence to these supernatants to evaluate S. aureus lysis. (D) Role of the pqs pathway in hypoxic conditions. Spots of P. aeruginosa cultures were deposited on LB agar plates cover by a S. aureus lawn. Plates were incubated during 48 h in hypoxic conditions.
