Fig 2.
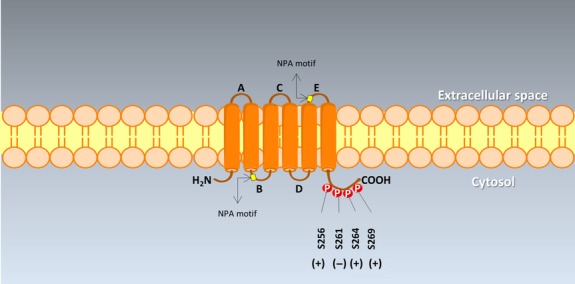
The topology of AQP2 with the COOH-terminal phosphorylation sites. AQP2 is a tetramer consisting of four identical protein subunits placed in the plasma membrane. Six transmembrane α-helices are arranged in a right-handed bundle and are represented by cylinders, with the amino (NH2-) and the carboxyl (COOH-) termini located on the cytoplasmic surface of the membrane. Five interhelical loop regions (A–E) form the extracellular and cytoplasmic vestibules. Loops B and E are hydrophobic loops that contain the highly, although not completely conserved, asparagine–proline–alanine (NPA) motifs. Such motifs appear to dip and overlap into the membrane, to construct the water pore 33,90. Serine residues at potential phosphorylation sites are labelled with their amino acid numbers at the carboxyl-terminal tail. AVP mediated increased (+) phosphorylation at S256, S264 and S269, and decreased (−) phosphorylation at S261. Both S269 and S256 phosphorylation are involved in AQP2 accumulation in the plasma membrane 50,246,247.
