Figure 3. Antimicrobial effects of granulysin peptides with d- and l-type amino acids.
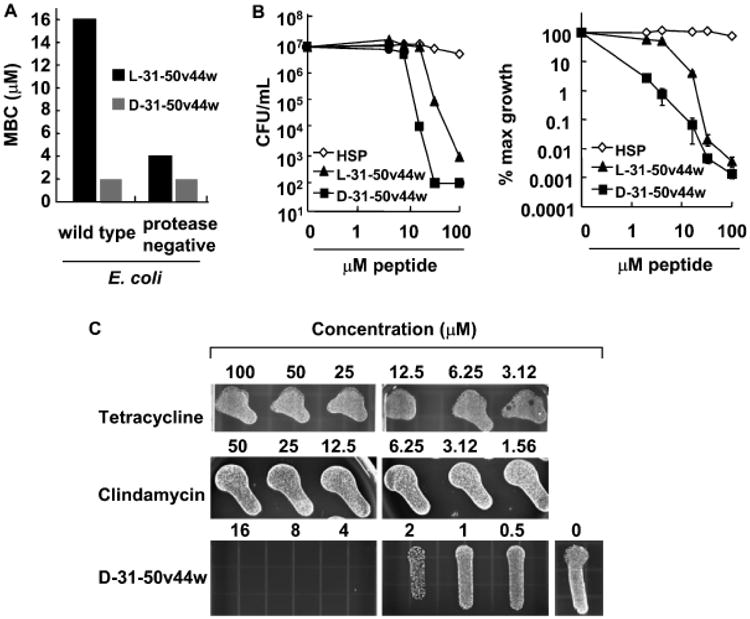
(A) Granulysin peptides with the sequence 31–50v44w were synthesized using only d-type amino acids (d-31–50v44w) or l-type amino acids (l-31–50v44w) and incubated with a wild-type strain of Escherichia coli or a mutant strain of E coli, and the minimum bactericidal concentration was determined. (B) Granulysin peptides with d-type amino acids (d-31–50v44w) or l-type amino acids (l-31–50v44w) were incubated with P. acnes and the antimicrobial activity was determined using CFU assay (left, representative experiment; right, average % maximum growth ± SEM, n = 4). (C) The antimicrobial activity of granulysin peptide d-31–50v44w was compared to tetracycline and clindamycin in a qualitative CFU assay which involved plating antibiotics and peptides with P. acnes on solid media and counting individual colonies to determine the CFU. Experiments in (A) and (C) are representative of two or more experiments.
