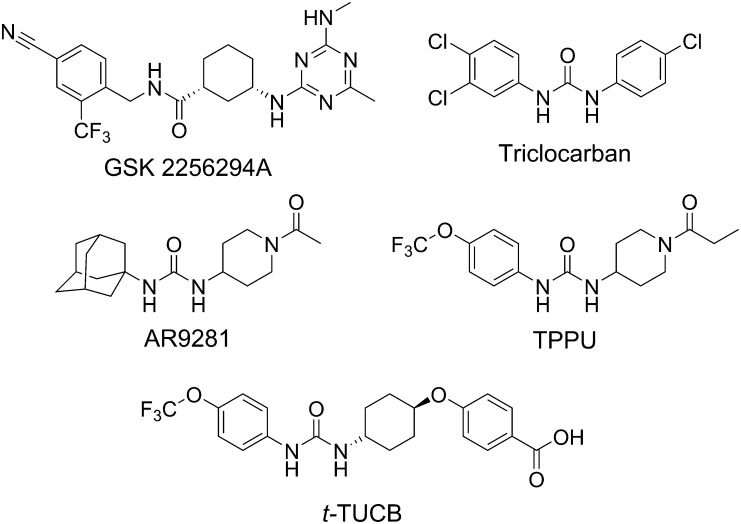
Fig. 6.
IND and development candidates among sEH inhibitors. GSK2256294 is a potent inhibitor that has demonstrated efficacy in vivo and is in the clinic (Podolin et al., 2013). Triclocarban is a commonly used antimicrobial that also inhibits the human sEH (Schebb et al., 2011) and has proved successful as a topical analgesic when used with diclofenac in a double-blind clinical trial for diabetic neuropathic pain. AR9281 (UC11A53, APAU), originally reported by Jones et al. (2006), was taken through phase 2A for hypertension and metabolic syndrome (Anandan et al., 2011). AR9281 is more potent on the rat recombinant sEH than the human sEH, has poor target occupancy of the human sEH, and has a short half-life due to rapid P450 metabolism of the adamantane moiety. TPPU (UC1770) shows high potency in rodent and primate species and has been provided to many laboratories as a model sEH inhibitor (Ulu et al., 2012). t-TUCB (UC1728) is in trials for the neuropathic pain of equine laminitis (Guedes et al., 2013) and is being evaluated for canine arthritis and feline joint pain. TPPU, 1-trifluoromethoxyphenyl-3-(1-propionylpiperidin-4-yl)urea; t-TUCB, trans-4-{4-[3-(4-trifluoromethyoxy-phenyl)-ureido]-cyclohexyloxy}benzoic acid.