TABLE 2.
Experimentally important substrates of epoxide hydrolases
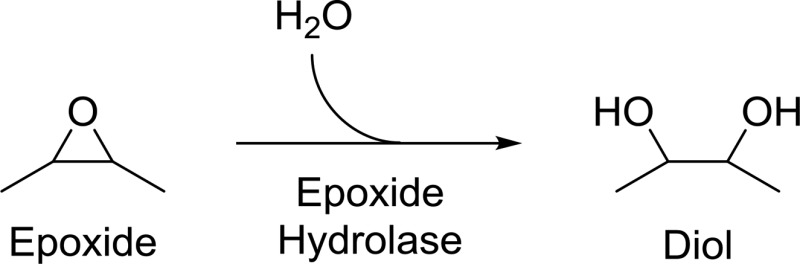
Epoxide hydrolases convert the 3-membered cycle ether of the epoxide in a downhill reaction adding water to generate a 1,2- or vicinal diol. Historically, a number of substrates have been experimentally important for both characterizing epoxide hydrolases and studying their physiologic importance. Kinetic studies using these substrates have primarily been performed only in a few species, so care must be taken when generalizing results across species.
| Name | Structure | Primary Hydrolyzing Enzyme |
|---|---|---|
| Styrene oxide | 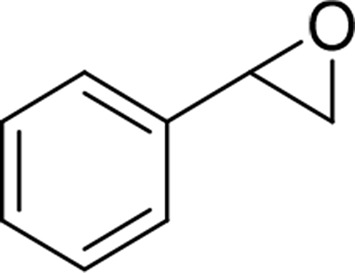 |
mEH and sEH |
| trans-β-ethyl-styrene oxide | 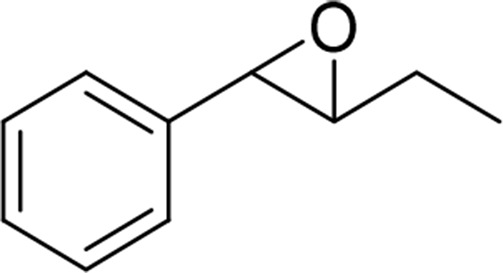 |
sEH |
| Allylbenzene oxide | 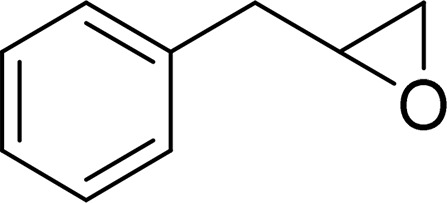 |
mEH and sEH |
| cis-Stilbene oxide (CSO) | 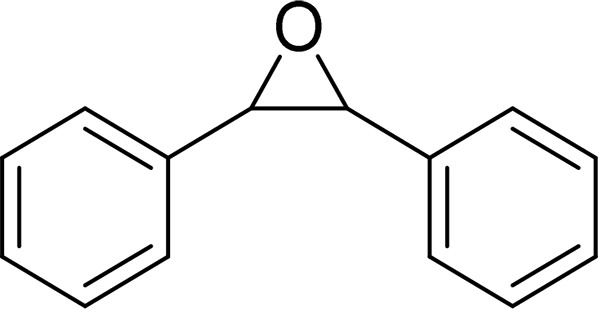 |
mEH |
| trans-Stilbene oxide (TSO) | 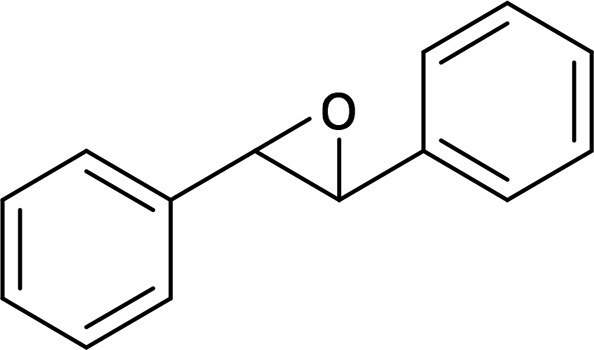 |
sEH |
| trans-Diphenylpropene oxide (t-DPPO) | 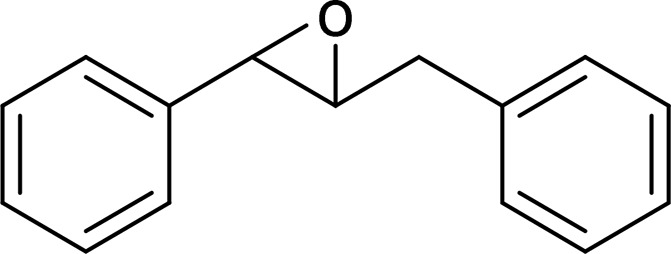 |
sEH |
| Cyano(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)methyl-trans-[(3-phenyloxiran-2-yl)methyl] carbonate (CMNPO) | 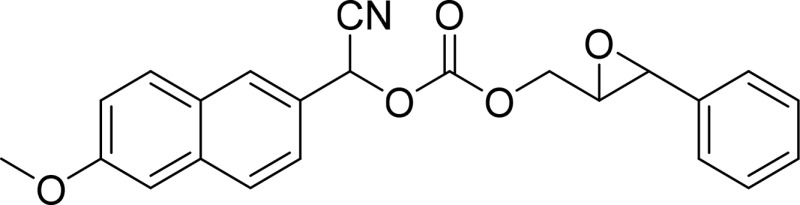 |
sEH |
| Leukotoxin | 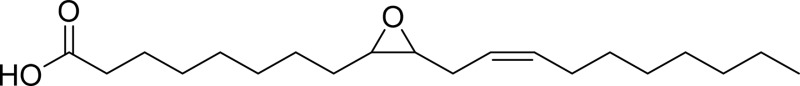 |
sEH |
| 11,12- EET |  |
sEH |
| 19,20-EpDPE | 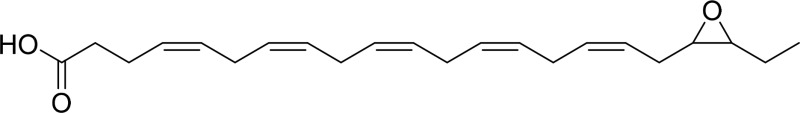 |
sEH |
| Juvenile hormone III (JH3) | 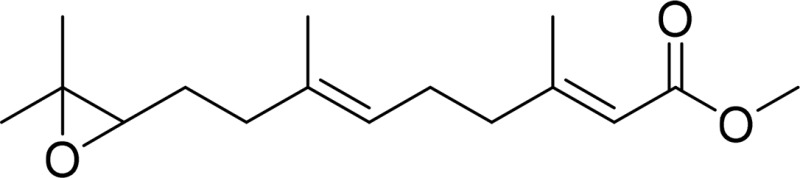 |
Juvenile hormone epoxide hydrolase sEH |
| 5,6-Cholesterol epoxide | 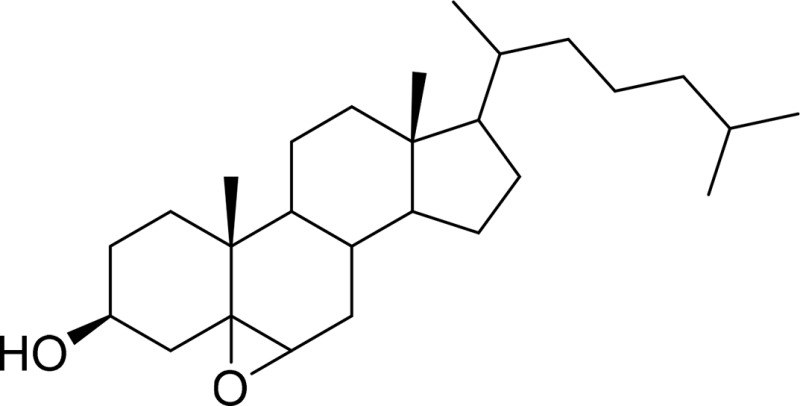 |
ChEH |
