Figure 1. Proposed model for fatty acid stimulation of SIRT6 activity.
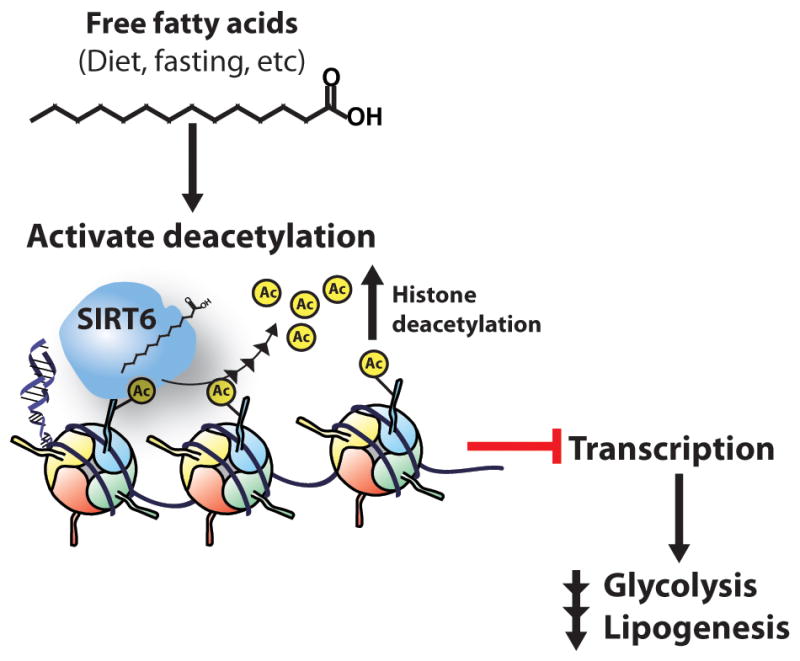
SIRT6-dependent deacetylation is stimulated by free long-chain fatty acids obtained through diet or from fasting, which leads to increased transcriptional repression and downregulation of glycolytic and lipogenic genes.
