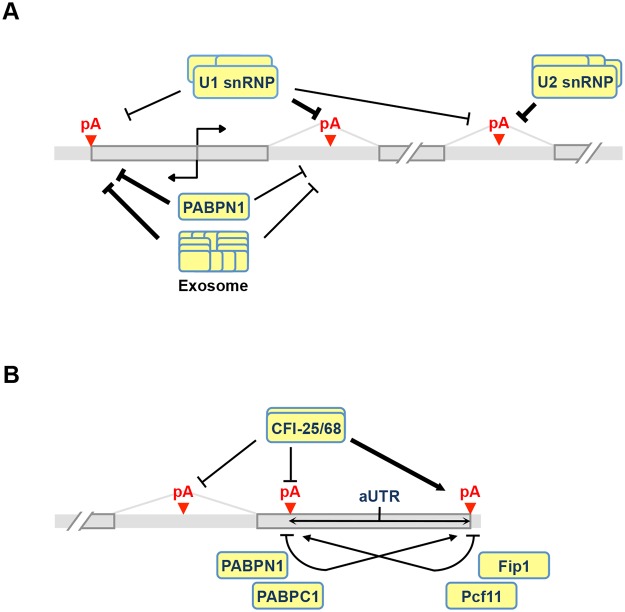
Fig 8. APA models.
(A) Regulation of C/P events near the transcription start site (TSS) and introns. Both U1 and PABPN1 inhibit polyA(+) transcript expression near the TSS. For U1, inhibition of sense strand RNA is more prominent than that of upstream antisense RNA (uaRNA) due to higher frequency of its binding sites, i.e., 5’ splice site or related sequences, in the sense strand. The mechanism is likely to be inhibition of polyadenylation. PABPN1 has the opposite trend, with suppression of uaRNA expression being more significant. This function of PABPN1 is likely to involve exosome-mediated RNA decay. U1 and U2 inhibit intronic C/P because C/P is in a kinetic competition with splicing. (B) Regulation of pA usage in the last intron and the 3’-most exon. CFI-25/68 promotes usage of distal pAs through binding to the UGUA element, leading to longer 3’UTRs and selection of downstream terminal exons. PABPN1 and PABPC1 also promote distal pA usage, whereas Pcf11 and Fip1 promote proximal pA usage. Note that if two pAs are close to each other and there is an AAUAAA motif downstream of the proximal pA, Fip1 helps select the distal pA (not indicated in the graph). aUTR size is indicated to highlight its importance in APA regulation.