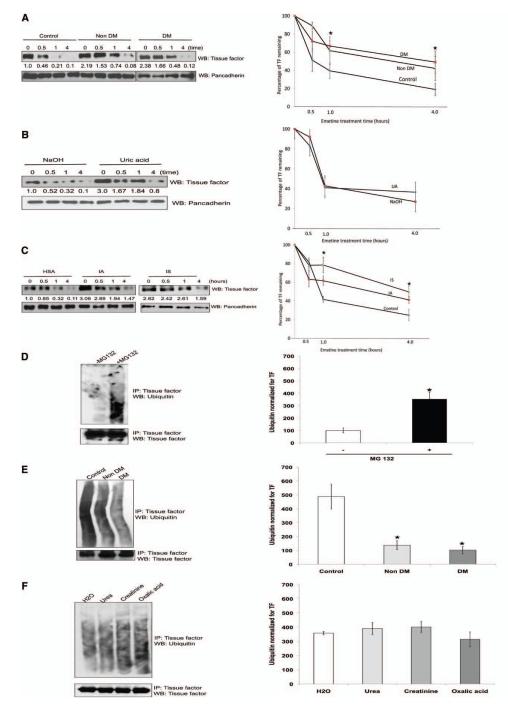
Figure 5.
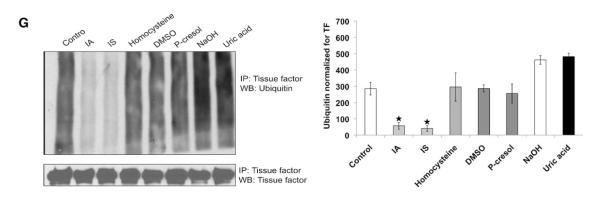
Uremic serum stabilizes tissue factor (TF) by inhibiting its ubiquitination, and indole-3-acetic acid (IA) and indoxyl sulfate (IS) recapitulate its effect on TF. A, Both nondiabetic and diabetic uremic sera increase TF half-life. Vascular smooth muscle cells (vSMCs) treated with pooled 5% control or nondiabetic or diabetic uremic sera for 24 hours are shown. Emetine 20 μmol/L was used for indicated time. The cells were harvested, and TF expression was analyzed by immunoblotting. Representative blot from 3 experiments is shown. Densitometry was performed on half-life study with the use of Image J, and pancadherin was used to normalize the TF signal. Average of 3 experiments is shown. *P value is 0.03 for both the DM and non-DM sera treated vSMCs compared to the control. Error bars=SEM. DM indicates diabetes mellitus. B, Uric acid does not affect half-life of TF. vSMCs treated with NaOH and uric acid for 24 hours were treated with emetine as above. Representative blot from 3 experiments is shown. Densitometry was performed on half-life study with Image J, and pancadherin was used to normalize the TF signal. *P value is 0.02 for both the IA and IS treated vSMCs compared to the control. Average of 3 experiments is shown. Error bars=SEM. C, IA and IS prolong half-life of TF. vSMCs exposed to protein-bound solutes and control (treated with human serum albumin [HSA]) for 24 hours were treated with emetine for indicated time. The cells were harvested, and TF expression was analyzed by immunoblotting. Representative blot from 3 experiments is shown. Densitometry was performed on half-life study shown in Figure 4F with the use of Image J, and pancadherin was used to normalize the TF signal. *P value is 0.02 for both the IA and IS treated vSMCs compared to the control. Average of 3 experiments is shown. Error bars=SEM. D, Ubiquitination of endogenous TF. vSMCs 1·106 were treated with MG132. TF was immunoprecipitated (IP) with the use of TF antibody and immunoblotted with ubiquitin antibodies. Immunoprecipitated TF is shown as input. Representative immunoblot from 3 experiments is shown. Densitometry analysis was performed on ubiquitin smear normalized with immunoprecipitated TF with the use of Image J. Average of 3 experiments is shown. P<0.05 for ubiquitin without vs with MG132. Error bars=SEM. E, Uremic serum inhibits TF ubiquitination. vSMCs treated with 5% pooled control or nondiabetic or diabetic uremic sera for 24 hours were lysed after treatment with MG132. TF ubiquitination was examined as described above. Representative immunoblot from 3 experiments is shown. Densitometry analysis was performed on ubiquitin smear as described above. Average of 3 experiments is shown. P<0.05 for non-DM and DM uremic compared with control serum. Error bars=SEM. F, Water-soluble uremic solutes have no effect on TF ubiquitination. vSMCs were treated with uremic solutes for 24 hours and 10 μM MG132 for the last 6 hours. Water-treated sample served as control. Representative immunoblot from 2 experiments is shown. Densitometry analysis was performed as described above. Average of 2 experiments is shown. Error bars=SEM. G, IA and IS inhibit TF ubiquitination. vSMCs were treated with protein-bound uremic solutes or uric acid solutes for 24 hours and MG132. TF was immunoprecipitated as above. Human albumin or NaOH served as control. Representative immunoblot from 3 experiments is shown. Densitometry analysis was performed as described above. Average of 3 experiments is shown. P<0.05 for IA and IS compared with human serum albumin (control). Error bars=SEM. DMSO indicates dimethyl sulfoxide; and WB, westernblot.