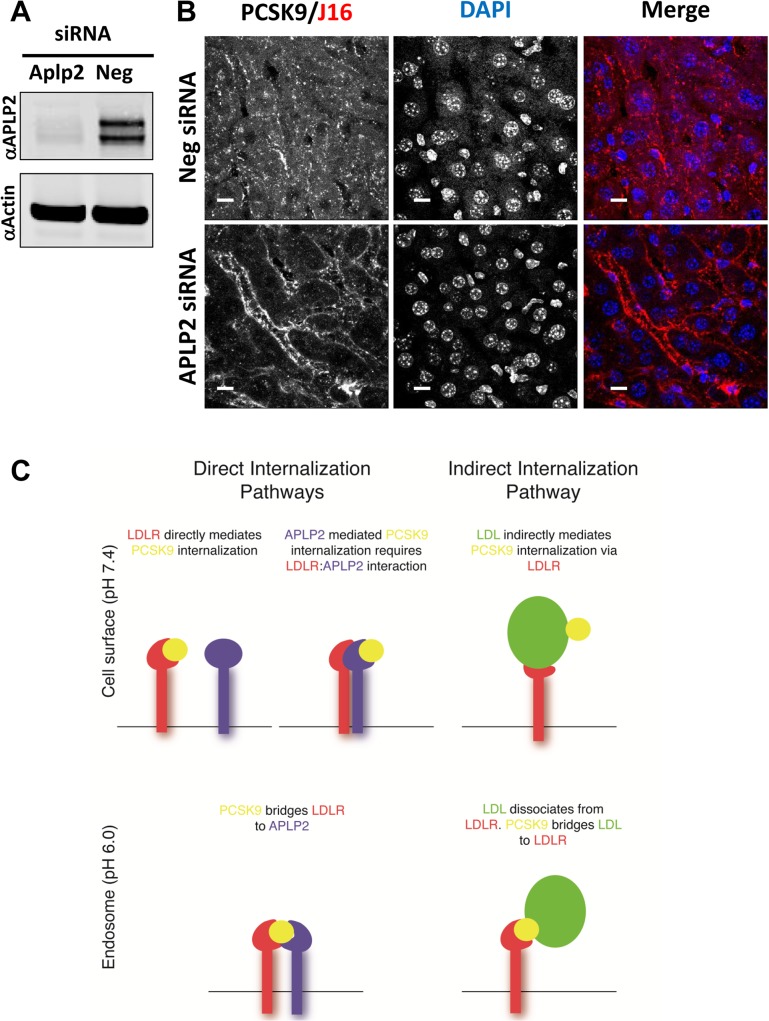
Fig 7. PCSK9 follows both direct and indirect internalization routes.
(A) Western blot of liver lysates taken from negative siRNA or APLP2 siRNA treated mice showing relative APLP2 levels as compared to Actin loading control. (B) Internalization of J16 bound PCSK9 in liver in negative or APLP2 siRNA treated mice. Scale bars, 10 μM. (C) Schematic depicting interactions of the proposed direct and indirect PCSK9 internalization routes. At the cell surface, PCSK9 can bind directly to LDLR or APLP2; PCSK9 binding to APLP2 requires LDLR/APLP2 interactions. For both direct routes, following endocytosis, PCSK9 bridges LDLR to APLP2, and APLP2 mediates lysosomal delivery of the complex. Indirect PCSK9 internalization is mediated via LDL. PCSK9 binds LDL, and LDL binds LDLR at the cell surface. Following endocytosis, PCSK9 can potentially bridge dissociated LDL to LDLR.