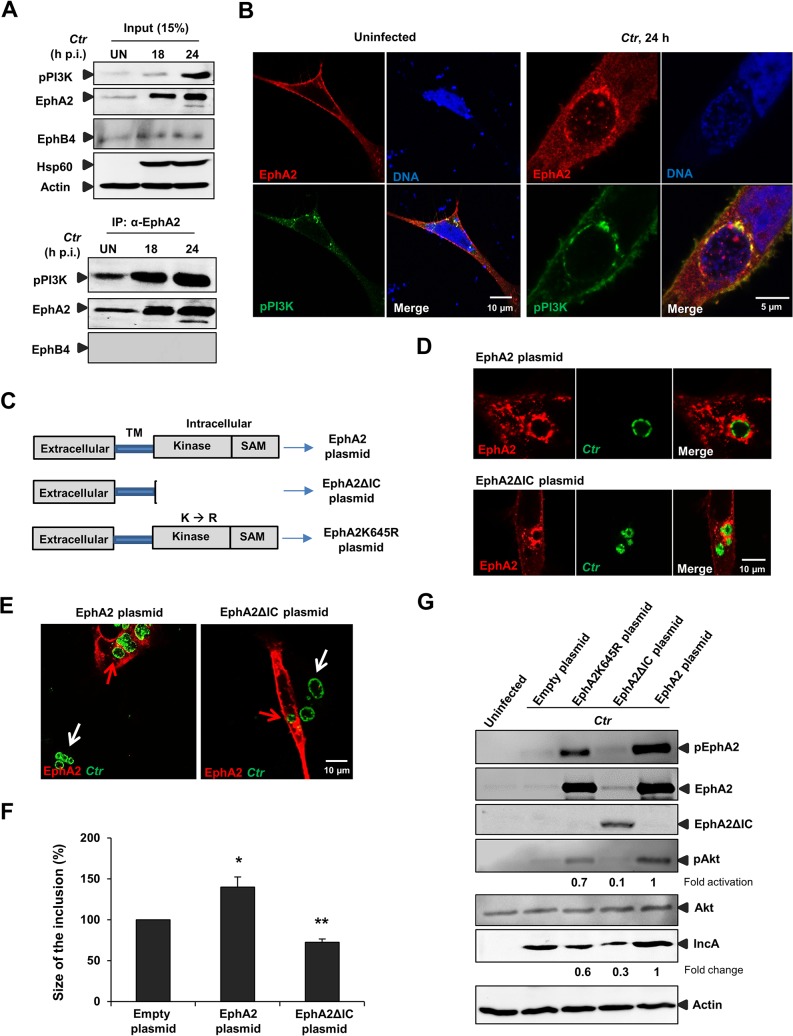
Fig 6. EphA2 intracellular cytoplasmic domain is crucial for Ctr infection.
(A) HeLa cells were left UN or infected with Ctr (MOI-2) for the indicated period of times and immunoprecipitated using α-EphA2 antibody. The IP material was solved in 40 μl Laemmli (100%) and loaded 20 μl for WB studies (50%). (B) Cells were transfected with EphA2-pcDNA3 and p85-PI3K expression plasmid together for 15 h followed by Ctr infection for 24 h. Cells were stained against EphA2 (red), DNA (blue) and pPI3K (green). (C) Schematic representation of full length EphA2 plasmid, EphA2 kinase dead mutant plasmid (EphA2K645R) and EphA2 mutant plasmid missing the entire cytoplasmic domain (EphA2ΔIC). TM: transmembrane domain. (D) The plasmids having full length EphA2 or EphA2ΔIC were transfected and these cells were infected with Ctr for 20 h. Cells were fixed and stained against α-EphA2 antibody (red) and Ctr using α-Hsp60 (green). (E) Arrows were marked to illustrate the difference between the size of the inclusion of untransfected (white arrows) and transfected (red arrows) cells. (F) Size of the inclusion for (E) was determined by ImageJ software. Empty-plasmid transfected cells act as a control. Shown is the mean ± SD of two independent experiments normalized to empty-plasmid transfected cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. Error bars show mean ± SD. (G) Cells after transfection of the constructs (each 1.5 μg/ml) indicated above the lanes followed by infection (MOI-1) for 18 h were subjected to WB analysis to analyze the proteins as indicated. EphA2ΔIC was detected by N-terminal EphA2 antibody. Due to the high intensity of total EphA2 and phospho EphA2 from the EphA2-transfected infected cells, the upregulation of endogenous EphA2 cannot be visualized. (B, D, F) Magnification is indicated in size bar.