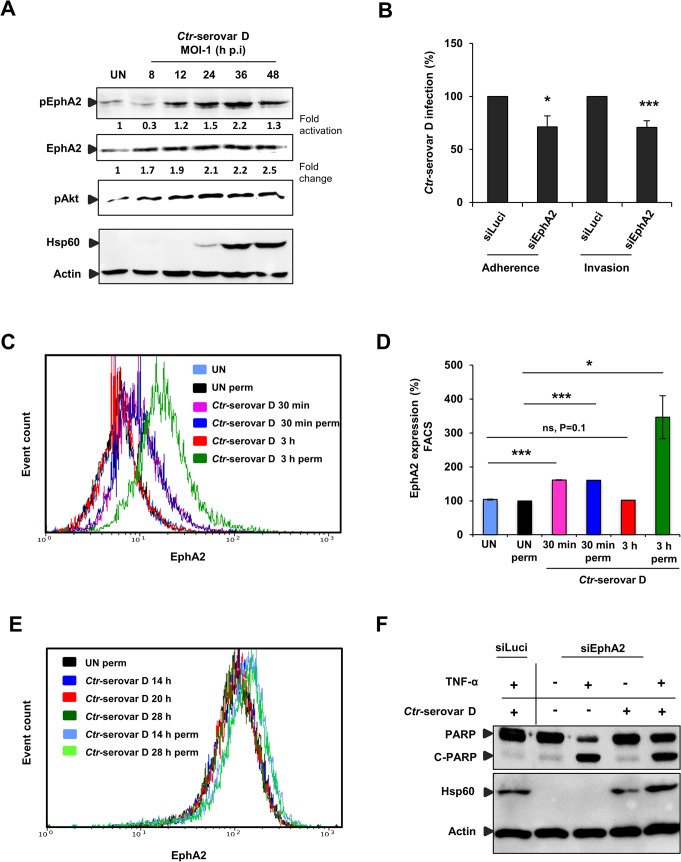
Fig 10. Ctr-serovar D utilize EphA2 signaling to invade the cells and to prevent apoptosis induced by TNF-α.
(A) HeLa cells left UN or infected with Ctr-serovar D were centrifuged at 910 x g for 30 min and allowed to infect for the indicated time points. The cells were harvested and subjected to WB analysis. (B) HeLa cells were transfected with siRNA against luciferase gene (siLuci) or EphA2 gene (siEphA2) for 40 h at 37°C. Adherence assay: The transfected cells were infected with Ctr-serovar D for 1 h at 4°C. Cells were immunostained against EB and Actin filaments. Number of extracellular EB was counted randomly from 30 different cells. Data are expressed as percentage of extracellular EB relative to siLuci. Shown is the mean ± SD of three independent experiments normalized to siLuci. *P<0.05. Error bars show mean ± SD. Invasion assay: The transfected cells were infected with Ctr-serovar D for 4–5 h at 35°C. Cells were immunostained against EB and Actin filaments. Number of invaded EB was counted randomly from 30 different cells. Data are expressed as percentage of invaded EB relative to siLuci. Shown is the mean ± SD of three independent experiments normalized to siLuci. *P<0.001. Error bars show mean ± SD. (C) FACS analysis was performed with Ctr-serovar D infected cells as Fig 3A. (UN: uninfected, Iso: isotype and perm: permeabilised). (D) Results of C were shown as bar charts. Shown is the mean ± SD of two independent experiments normalized to UN. ***P<0.001, *P<0.05, ns: non-significant. Error bars show mean ± SD. (E) HeLa cells were left UN or infected with Ctr-serovar D (MOI-1) for 14, 20 and 28 h and cells were analyzed via FACS as Fig 4A. (F) EphA2 knockdown followed by 16 h Ctr-serovar D infected cells were induced to apoptosis by TNF-α (50 ng/ml)/CHX (5 μg/ml) for 5–6 h. Processing of PARP, Hsp60 and Actin were monitored by WB analysis.