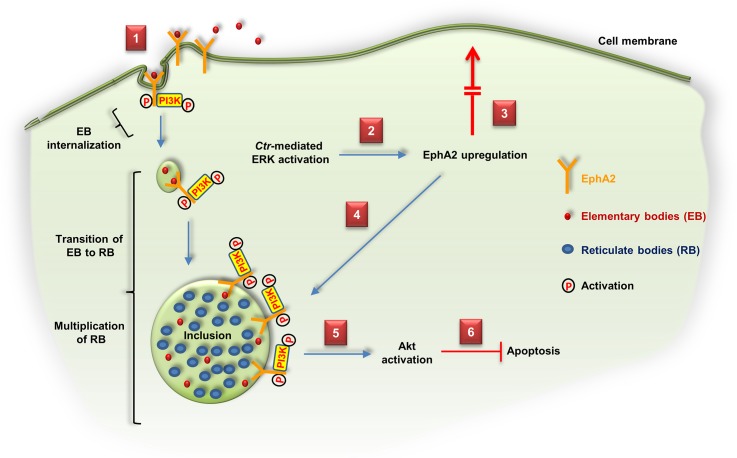
Fig 11. Schematic model depicting the role of EphA2 as an invasion and intracellular signaling receptor for C. trachomatis.
(1) Ctr-EB bind and activate EphA2 and enter the cell together with the activated receptor and PI3K recruited to EphA2. (2) Ctr-mediated ERK activation induces EphA2 upregulation. (3) Upregulated EphA2 does not appear at the cell surface. (4) Intracellular EphA2 is associated with the Ctr inclusion which interacts with pPI3K. (5, 6) EphA2-induced signaling cascades (pAkt) are required to inhibit apoptosis and enhance the infection.