Fig 5.
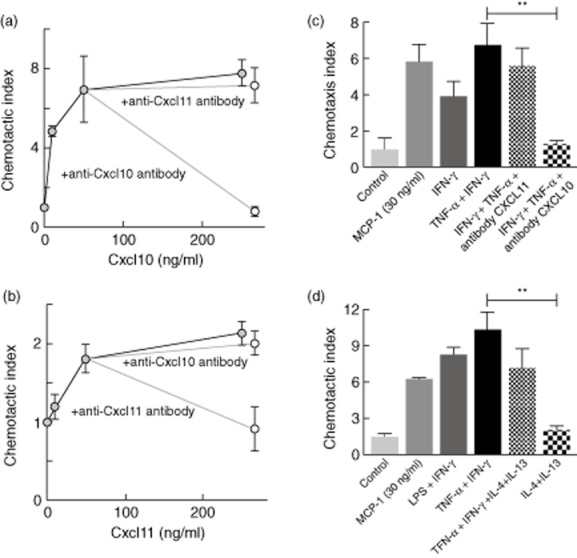
CXCL10 produced by cultured human podocytes in response to interferon (IFN)-γ and tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α induces monocyte migration. The chemotactic index was calculated as the fold increase, compared to sham-treated controls, in the number of THP-1 monocytes migrating across a 5-μm-pore membrane in response to chemoattractants. (a) Migration after incubation over wells containing various concentrations of recombinant CXCL10, or with 250 ng of CXCL10/ml preincubated with neutralizing antibodies against CXCL10 or CXCL11. (b) Migration after incubation over wells containing various concentrations of recombinant CXCL11, or with 250 ng of CXCL11/ml preincubated with neutralizing antibodies against CXCL10 or CXCL11. (c) Migration after incubation over wells containing culture supernatants from human podocytes collected 24 h after a 6 h treatment with IFN-γ, or TNF-α + IFN-γ. (d) Migration after incubation over wells containing culture supernatants from human podocytes collected 24 h after a 6 h treatment with either type 1 stimulation [lipopolysaccharide (LPS) + IFN-γ, or TNF-α + IFN-γ] or type 1 + type 2 stimulation (TNF-α + IFN-γ + IL-4 + IL-13) or type 2 cytokines only (IL-4 + IL-13). Control supernatants are from untreated podocyte cultures. The chemoattractant CCL2 [monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1)] was used as positive control. Results are expressed as mean ± standard error, n = 4/group; **P < 0·01 compared to control.
