Fig 5.
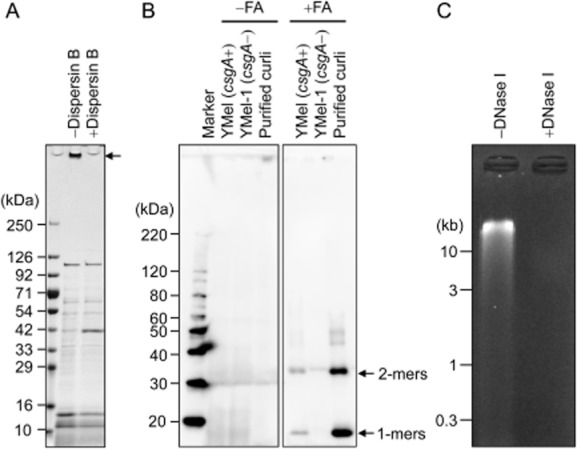
Applicability of the ECM extraction method to S. epidermidis, E. coli and P. aeruginosa biofilms.A. Extracellular matrices extracted from S. epidermidis SE04 by the addition of 1.5 M NaCl were treated with or without dispersin B and were then applied to SDS-APGE. The gel was stained with CBB. An arrow indicates polysaccharides.B. Extracellular matrices of E. coli YMel and its isogenic csgA mutant YMel-1 were isolated with 1.5 M NaCl. Curli amyloid fibres in the ECM fraction were treated with or without formic acid. Purified curli was also used as a positive control. The proteins were analysed by Western blotting using anti-CsgA antibody. Arrows indicate monomeric and dimeric CsgA. FA, formic acid.C. Extracellular matrices of P. aeruginosa PAO1 were extracted with 1.5 M NaCl and were subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis. The extracted ECMs were treated with or without DNase I. The gel was stained with ethidium bromide. The positions of molecular mass markers in kilodaltons (kDa) (A and B) and kilobase pairs (kb) (C) are shown at the left of each panel respectively.
