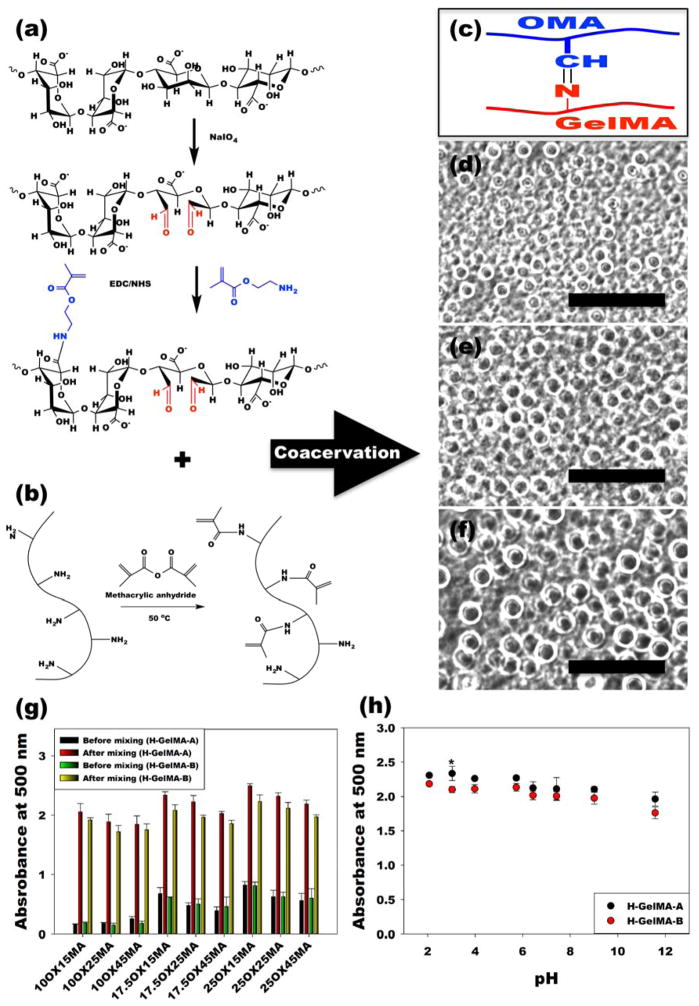
Figure 1. Formation of OMA/GelMA coacervates.
(a–b), Schematic illustrations of preparation and chemical structures of (a) OMA and (b) GelMA. (c) Schematic illustration of Schiff base reaction between the aldehyde group of the OMA and amine group of the GelMA. (d–f), Representative optical photomicrographs of OMA/GelMA coacervate microdroplets formed by (d) 17.5OX15MA and H-GelMA-B, (e) 17.5OX25MA and H-GelMA-B, and (f) 17.5OX45MA and H-GelMA-B. The scale bars indicate 100 μm. (g) Turbidity of OMA/GelMA solutions prepared at pH 7.4 before and after mixing of two solutions by the measurement of the absorbance at 500 nm to evaluate the degrees of complex coacervate formation. (h) Turbidity of OMA (25OX45MA)/H-GelMA coacervate as a function of pH. All quantitative data is expressed as mean ± standard deviation (N=3). Statistical analysis was performed with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey significant difference post hoc test using Origin software (OriginLab Co). The absorbance of all groups significantly increased after mixing (p<0.001). *p<0.05 compared with H-GelMA-B at a specific pH.