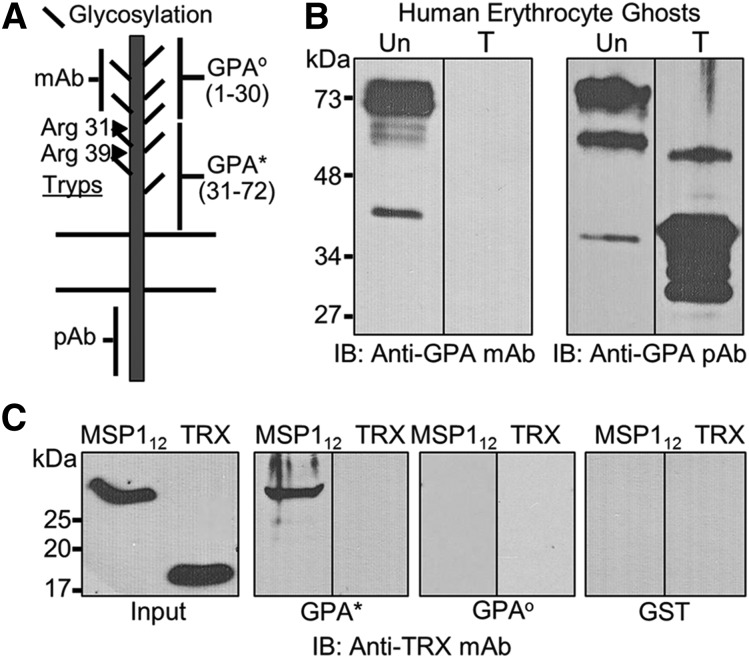
Figure 3.
Characterization of the MSP1-GPA interaction. (A) GPA, a single transmembrane protein, shows significant glycosylation in the extracellular domain that can be removed by neuraminidase treatment. The approximate locations of the sites recognized by the monoclonal antibody (mAb) and polyclonal antibody (pAb) are indicated. The trypsin cleavage of GPA occurs at 2 distinct arginine residues (Arg31 and Arg39) on the extracellular domain. The extracellular domain of GPA was expressed as 2 nonoverlapping contiguous segments designated as GPAo and GPA*. (B) Both untreated (Un) and trypsin-treated (T) erythrocyte ghosts were tested by immunoblotting (IB) using monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies against GPA. (C) Binding of MSP112 to the trypsin-resistant segment of GPA (GPA*, amino acids 31-72) was detected by immunoblotting against TRX. The trypsin-sensitive segment of GPA (GPAo, amino acids 1-30) was also expressed and tested under identical conditions. Because both fusion proteins contained the GST-tag, GST was also used as a negative control.