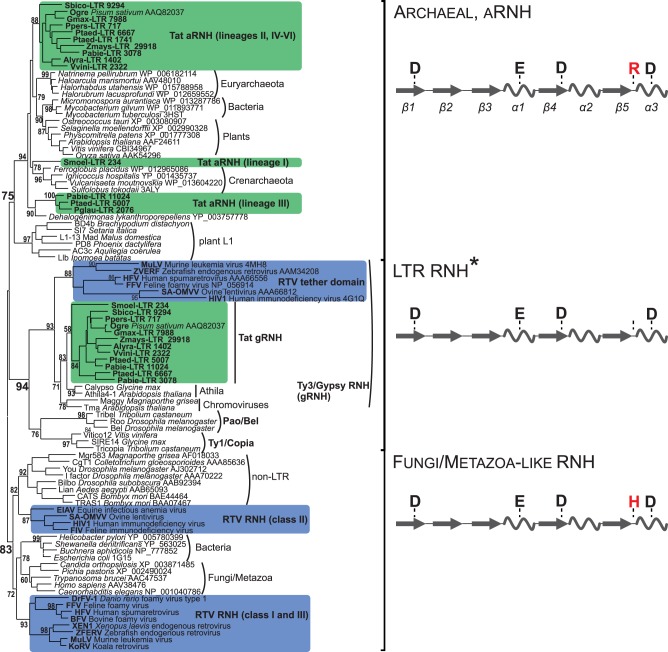
Fig. 3.
Maximum-likelihood tree based on the amino acid sequences of different types of type I RNHs. Statistical support was evaluated by the aLRT and is shown at the corresponding nodes of the tree. aRNH and gRNH from Tat LTR retrotransposons are highlighted in green. RNH and tether from retroviruses (RTV) are highlighted in blue. Schemes of the secondary structures of three subtypes of RNH with the corresponding active site residues are shown at the right of the tree. The α-helices are depicted as helices, and the β-sheets are shown as arrows. The conserved arginine (R) or histidine (H) residue of the active site, which is specific for different RNHs, is highlighted in red. *The positions corresponding to DEDD catalytic core residues are not conserved in the gRNHs of Tat LTR retrotransposons and tether domain of vertebrate retroviruses (see supplementary fig. S3, Supplementary Material online).