Figure 3.
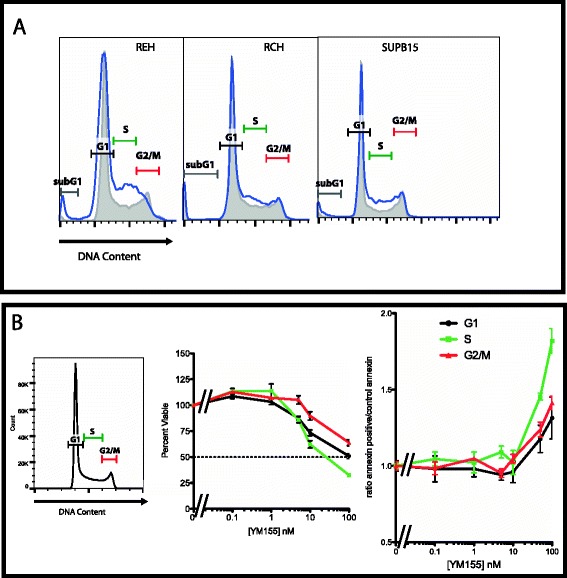
YM155 causes an S phase arrest. (A) Cell cycle arrest with YM155 treatment. An asynchronous population of cells (REH, RCH, and SUPB15) were treated with 100 nM YM155 for 24 h and assayed for DNA content by propidium iodide. (Grey line filled) Control asynchronous population. (Blue line) YM155 treatment. Bars indicate the cell cycle (subG1, G1, S, G2/M). All three cell lines show an increase in S phase and a slight increase in the sub G1 phase within 24 h of treatment. (B) YM155 treatment has a greater effect when exposed to cells that are in S phase of the cell cycle. An asynchronous REH population was sorted by DNA content for G1, S, and G2/M and treated with increasing concentration of YM155 (0 to 100 nM) for 24 h, then assessed for viability using an MTS colorimetric assay (middle panel) or for Annexin V staining (right panel).
