Table 1.
Essential oil phenylpropanoids with antitumoral activity.
| Compound | Experimental protocol | Antitumoral activity and/or mechanism | Animal/cell line tested | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
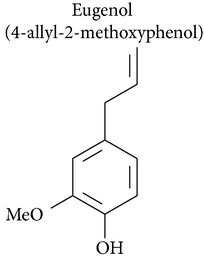
|
Anaphylaxis model | Apoptotic manifestations via phospho-ser 15-p53 into mitochondria | Mast cells | [11] |
| Skin carcinogenesis model | Inhibition of the proliferation associated genes c-Myc and H-ras and antiapoptotic gene Bcl2 along with upregulation of proapoptotic genes Bax, p53, and active caspase-3 | Mice | [12] | |
| Trypan-blue assays | Cytotoxic activity | B16-F10, Sbcl2, WM3211, WM98-1 and WM1205Lu, PC-3, human gingival fibroblasts, oral mucosal, neutrophils—male guinea pig, rat hepatocytes cells | [14, 15, 23, 32, 33, 48, 49] | |
| Melanoma cell proliferation | Deregulation of the E2F family of transcription factors, transcriptional activity of E2F1 | Sbcl2, WM3211, WM98-1, and WM1205Lu cells | [15] | |
| Flow cytometry analysis | Cytotoxic activity | P-815, K-562, CEM, and MCF-7 cells | [13] | |
| VL irradiation time | Antioxidative reactivity | HSG, HSC-2, and HL-60 cells | [17] | |
| MTT assay | Cytotoxic activity | B16-F10, P-815, K-562, CEM, MCF-7, MCF-7 gem, HeLa, DU-145, KB, HSG, human dental pulp, murine peritoneal macrophages HL-60, HepG-2, B16, cells | [13, 19–22, 25–29, 38, 45, 46, 48] | |
| DPPH assay | Antioxidative activity | Caco-2 cells and VH10 fibroblasts | [18] | |
| Flow cytometer analysis | Enhanced the accumulation of cells in the S and G2/M phase which may be unable to divide | HeLa cells | ||
| DAPI staining | Increase in the number of apoptotic cells | |||
| In vitro hemolytic activity | Hemolytic activity | Human erythrocytes | [19] | |
| Caspase-3 colorimetric assay | Induce caspase 3-mediated apoptosis | |||
| RT-PCR | Anticancer activities via apoptosis induction and anti-inflammatory downregulation of Bcl-2, COX-2, and IL-1β | |||
| RT-PCR | Downregulated the expression of Bcl-2, COX-2, and IL-β | HeLa cells | [20] | |
| Flow cytometer analysis | Increased population of cells G2/M phase by 4.5-fold | PC-3 cells | [24] | |
| Western blot and RT-PCR analysis | Reduced expression of antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 and enhanced expression of proapoptotic protein Bax | |||
| DPPH radical-scavenging activity | Formation of dimers | HSG cells | [25] | |
| ELISA | Reduced the nicotine-induced ROS, NO generation, and iNOSII expression | Murine peritoneal macrophages | [27] | |
| Spectrophotometric analysis | Increase in LDH release | DU-145 and KB cells | [28] | |
| ESR analysis | Activity of the production of phenoxyl radicals with most efficiently scavenged reactive oxygen | HSG cells | [29] | |
| Laser cytometry analysis | Production of ROS induced by VL-irradiated is significantly affected by pH | |||
| Antioxidants production | Produced antioxidants in alkaline solutions | Human salivary gland and oral squamous cells | [30] | |
| DPPH assay | Apoptosis-inducing effect | HGF and HSG cells | [31] | |
| TBA analysis lipid oxidation | Depleted intracellular glutathione; protect cells from the genetic attack of reactive oxygen species via inhibition of xanthine oxidase activity and lipid peroxidation | Oral mucosal fibroblasts | [32] | |
| ATP assay | Decreased cellular ATP level in a concentration- and time-dependent manner | |||
| NR assay | Intracellular glutathione levels | HFF and HepG2 cells | [33] | |
| Dichlorofluorescein assay | Reduction in the intracellular level of GSH | HSG cells | [34] | |
| CAs assay | Induced a dose-dependent increase of aberrant cells | V79 cells | [41] | |
| Topo II activity assay | Inhibition of topoisomerase II | |||
| Croton oil induced skin carcinogenesis | Inhibition of the proliferation associated genes c-Myc and H-ras and antiapoptotic gene Bcl2 along with upregulation of proapoptotic genes Bax, p53, and active caspase-3 | Swiss mice | [36] | |
| DMBA/TPA-induced carcinogenesis in murine skin | Declined of hyperplasia, epidermal ODC activity, and protein expression of iNOS, COX-2, and secretion of proinflammatory cytokines | Swiss mice | [42] | |
| TUNEL assay | Upregulation of p53 expression with a concomitant increase in p21WAF1 levels in epidermal cells indicating induction of damage to the DNA | |||
| Flow cytometric analysis | cDNA array analysis showed that eugenol caused deregulation of the E2F family of transcription factors | WM1205Lu cells | [24] | |
| TUNEL assay | Induces apoptosis in melanoma tumors | WM1205Lu cells | ||
| DPPH assay | Antioxidative properties | HL-60 and HepG-2 cells | [48] | |
| Sulforhodamine B assay | Cytotoxic activity | SK-OV-3, XF-498, and HCT-15 cells | [76] | |
| Murine Ehrlich ascites and solid carcinoma models | Inhibit the growth of Ehrlich ascites | BALB/c mice | [44] | |
| DPPH assay | Antioxidation activity | HepG2 cells | [22] | |
| Western blot analysis | Decreased the protein expression of BSP in a concentration-dependent manner | Human dental pulp cells | [35] | |
| DPPH assay | Antioxidant effect | Raw 264.7 cells | [43] | |
| VL irradiation/MTT assay | Generation of eugenol radicals | HSG and HGF cells | [36] | |
| Laser cytometer | Generation of ROS | |||
| ESR analysis | Produced phenoxyl radicals | HSG and HGF cells | [37] | |
| Superoxide generation/spectrophotometer | Stimulation the production of superoxide (O2 −) | Neutrophils—male guinea pig | [40] | |
|
| ||||
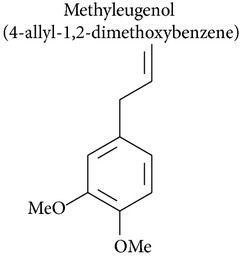
|
DPPH assay | Antioxidative properties | HL-60 and HepG-2 cells | [48] |
| UDS assay | Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity effects | B6C3F1 mouse hepatocytes | [47] | |
| F-344 rat hepatocytes | ||||
| L-Lactate assay | Cytotoxic effect | B6C3F1 mouse hepatocytes | ||
| F-344 rat hepatocytes | ||||
| MTT assay DPPH assay |
Cytotoxic activity Antioxidative properties |
HL-60, HepG-2, WM266-4, SK-Mel-28, LCP-Mel, LCM-Mel, PNP-Mel, CN-MelA, and GR-Mel cells | [16, 48] | |
| WST assay SRB assay |
Cytotoxic and genotoxic properties | V79 cells | [49] | |
| Corn oil gavage | Carcinogenic activity is based on increased incidences of hepatocellular adenoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and hepatocellular adenoma or carcinoma (combined) | F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice | [50] | |
| Trypan-blue exclusion assay | Cytotoxic activity | Rat hepatocytes | [55] | |
|
| ||||
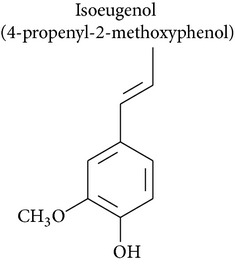
|
MTT assay |
Cytotoxic activity |
HSG cells | [29] |
| DPPH radical-scavenging activity | Cormation of dimers | |||
| Dichlorofluorescein assay |
Reduction in the intracellular level of GSH |
[39] | ||
|
| ||||
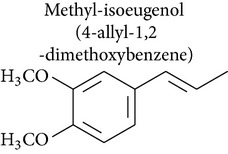
|
MTT assay | Inhibition of cell proliferation | WM266-4, SK-Mel-28, LCP-Mel, LCM-Mel, PNP-Mel, CN-MelA, and GR-Mel cells | [16] |
|
| ||||
|
WST assay SRB assay |
Cytotoxic and genotoxic properties | V79 cells | [49] |
|
| ||||
|
L-Lactate assay | Cytotoxic effect | B6C3F1 mouse hepatocytes | [47] |
| F-344 rat hepatocytes | ||||
| UDS assay | Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity effects | B6C3F1 mouse hepatocytes | ||
| F-344 rat hepatocytes | ||||
| Trypan-blue exclusion assay | Potential cytotoxic effects | Rat hepatocytes and SCC-4 cells | [47, 51, 54] | |
| Flow cytometric assay | Induction of apoptosis of cells by involvement of mitochondria- and caspase-dependent signal pathway | SCC-4 cells | [51] | |
| Western blotting analysis | Upregulation of the protein expression of Bax and Bid and downregulation of the protein levels of Bcl-2 (upregulation of the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2), resulting in cytochrome c release, promoted Apaf-1 level, and sequential activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3 in a time-dependent manner | |||
| Real-time PCR | mRNA expressions of caspases 3, 8, and 9 | |||
| MTT assay | Cytotoxic effect | Human BMFs | [52] | |
| Western blot analysis | Activate NF-κB expression that may be involved in the pathogenesis of OSF and mediated by ERK activation and COX-2 signal transduction pathway | |||
| Fura-2 as a probe assay | Induced a [Ca2+]i increase by causing Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum in a phospholipase C- and protein kinase C-independent fashion and by inducing Ca2+ influx | PC3 cells | [53] | |
| Comet assay/(DAPI) staining | Induced apoptosis (chromatin condensation) and DNA damage | HL-60 cells | [51] | |
| Flow cytometric analysis | Increased the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and Ca2+ and reduced the mitochondrial membrane potential | |||
| Western blotting analysis/confocal laser microscopy | Promoted the expression of glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78), growth arrest- and DNA damage-inducible gene 153 (GADD153), and activating transcription factor 6α (ATF-6α) | |||
| Flow cytometric analysis | Promoted the levels of CD11b and Mac-3 that might be the reason for promoting the activity of phagocytosis; reduced the cell population such as CD3 and CD19 cells |
NK cells | [58] | |
| Ames test | Mutagenicity activity | Salmonella TA 98 | [59] | |
|
| ||||
|
MTT assay |
Produced toxicity in cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner |
HepG2 cells FVB mice |
[56] |
| Comet assay | Significant dose-dependent increase in the degree of DNA (strand breaks) | |||
| Cytotoxic or genotoxic effect in vivo—i.p./Comet assay | Increase in mean Comet tail moment in peripheral blood leukocytes and in the frequency of micronucleated reticulocytes | HepG2 cells FVB mice |
||
| TUNEL assay | Activity of caspases 3, 8, and 9 | A549 cells | [58] | |
|
| ||||
|
Western blot assay | Cleavages of PARP, accompanied by an accumulation of cytochrome c and by the activation of caspase-3 | SK-N-SH cells | [60] |
|
| ||||
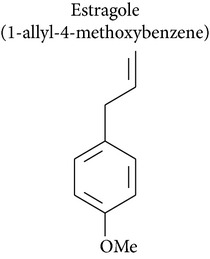
|
Induction of GST and QR |
Induction of GST and QR in mouse livers |
Four strains of mouse: A/JOlaHsd, C57BL/6NHsd, BALB/cAnNHsd, and CBA/JCrHsd |
[61] |
| Trypan-blue exclusion assay |
Cytotoxic activity |
Rat hepatocytes |
[55] |
|
|
| ||||
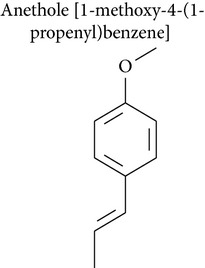
|
Trypan-blue assay | Cytotoxic activity | HeLa, rat hepatocytes cell | [21, 23, 55, 64] |
| MTT assay | Cytotoxic activity | HT-1080, ML1-a cells | [63] | |
| Boyden-chamber assay | Reduced 40 and 85% of cells to invade into Matrigel |
HT-1080 cells | [62] | |
| Gelatin zymography and RT-PCR analyses | Inhibitory effect of MMP-2 and MMP-9 and downregulate the expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) 2 and 9 and upregulate the gene expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase- (TIMP-) 1 | |||
| Expression of MMPs, TIMPs, and uPA assays | Decreased mRNA expression of urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) | |||
| Western blot analysis | Suppressed the phosphorylation of AKT, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), p38, and nuclear transcription factor kappa B (NF-κB) | |||
| Fluorometric assay | Increases in the levels of ADP and AMP | Rat hepatocytes | [62] | |
| CCK-8 assay | Estrogenic effect based on the concentrations of the hydroxylated intermediate, 4OHPB | MCF-7 cells | ||
| Western blot analysis | Suppressed TNF-induced activation of the transcription factor AP-1, c-jun N-terminal kinase, and MAPK-kinase | ML1-a cells | [63] | |
| Colorimetric e fluorometric assays | Reduced the levels of nucleic acids and MDA, and increased NP-SH concentrations | EAT cells in the paw of Swiss mice | [65] | |
|
| ||||
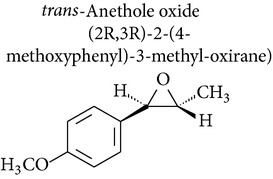
|
Ames test |
Mutagenic for Salmonella tester strains |
Salmonella typhimurium strains TA1535, TA100, and TA98 |
|
| Induction of hepatic tumors | Carcinogenic in the induction of hepatomas | B6C3F1 mice | [67] | |
| Induction of skin papillomas |
Carcinogenic in the induction of skin papillomas |
CD-1 mice |
||
|
| ||||
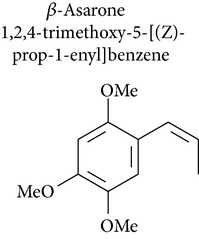
|
SRB assay | Cytotoxic activity | A549, SK-OV-3, SK-MEL-2, and HCT15 cells | [70] |
|
| ||||
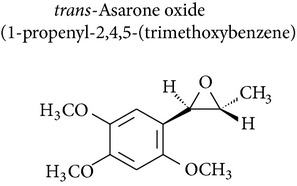
|
Ames test |
Mutagenic for Salmonella tester strains |
Salmonella typhimurium strains TA1535, TA100, and TA98 |
|
| Induction of hepatic tumors | Carcinogenic in the induction of hepatomas | B6C3F1 mice | [67] | |
| Induction of skin papillomas |
Carcinogenic in the induction of skin papillomas |
CD-1 mice |
||
|
| ||||
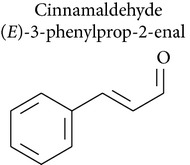
|
MTT assay | Cytotoxic activity | A375, HCT 116, MCF-7, P388, L-1210, 3LL, SNU-C5, HL-60, U-937, HCT 116, L1210 mouse, and Syrian hamster embryo cells | [71, 77, 78, 80, 84, 89] |
| TRPA1 and TRPM8 gene expression | Reduce the proliferation of melanoma cells; this effect is independent of an activation of TRPA1 channels | A375, G361, SK-Mel-19, SK-Mel-23, and SK-Mel-28 cells | [77] | |
| Sulforhodamine B assay | Cytotoxic activity | HeLa, A549, SK-OV-3, SK-MEL-2, XF-498, and HCT-15 cells | [76] | |
| Ames test | Not mutagenic | Strains (TA 98, TA 100, TA 1535, and TA 1537) of Salmonella typhimurium | ||
| DTNB assay | TrxR inactivation | Recombinant rat TrxR | [78] | |
| Western blot analysis | Induced an adaptive antioxidant response through Nrf2-mediated upregulation of phase II enzymes, including TrxR induction | HCT 116 cells | ||
| XTT assay | Inhibitory effects on the growth of cells | Hep G2 cells | [80] | |
| Western blot analysis | Increase in the CD95 (APO-1/CD95) protein expression in Hep G2 cells | |||
| Inhibited the expression of Bax, p53, and CD95, as well as the cleavage of PARP. This pretreatment also prevented the downregulation of Bcl-XL in cells | ||||
| Trypan-blue assay | Inhibited the proliferation of cells | PLC/PRF/5 cells | [81] | |
| Flow cytometer analysis | Activation of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family (Bax and Bid) proteins and MAPK pathway |
PLC/PRF/5 cells | [83] | |
| Western immunoblot analysis | Prevented the phosphorylation of JNK and p38 proteins | |||
| DAPI/Fluorometric method | Induced apoptosis in cells | P388, L-1210, 3LL, SNU-C5, HL-60, U-937, and HepG2 cells | [71] | |
| Flow cytometry analysis | Induces the ROS-mediated mitochondrial permeability transition and resultant cytochrome c release | |||
| cis-DDP-induced | Potentiated the inactivating effect of cis-DDP in all phases of the cell cycle | NHIK 3025 cells | [82] | |
| NRU assay | Induced the fragmentation of nuclei (Plate 2), which is typical for condensed apoptotic phenotype |
Hep-2 cells | [87] | |
| Genotoxicity assays—DNA repair test | Involve DNA damage as one of the factors involved in the mammalian cytotoxicity | |||
| LDH-cytotoxicity assay | Potent inhibitory effect against human hepatoma cell growth | HepG2 and Hep3B cells | [88] | |
| Western blot analysis | JAK2-STAT3/STAT5 pathway may be important targets | |||
| Decreased the protein levels of cyclin D1 and proliferative cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) but increased the protein levels of p27Kip1 and p21Waf1/Cip1 | ||||
| Flow cytometry analysis | Inducing apoptosis and synergizing the cytotoxicity of CIK cells | K562 cells | [92] | |
| Spectral analysis | Induced an adaptive antioxidant response through Nrf2-mediated upregulation of phase II enzymes, including TrxR induction | S180 in mice | [89] | |
|
| ||||
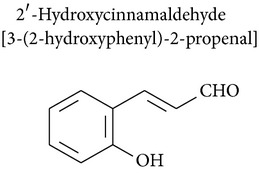
|
MTT assay | Cytotoxic activity | NIH/3T3 cells | [90] |
| Lymphoproliferation—Con A, LPS, or PMA plus ionomycin | Inhibit the lymphoproliferation and induce a T-cell differentiation from CD4CD8 double positive cells to CD4 or CD8 single positive cells | Mice splenocytes | [74] | |
| Flow cytometry analysis | Capability to block the cell growth and stimulate a differentiation to mature cell | |||
| IgM-secreting B cells to SRBC | Decreased level of IgM to be due to the lower level of B-cell proliferation | Balb/c mice | ||
|
| ||||
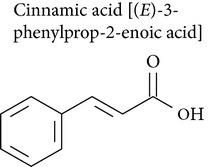
|
ELISA | Inhibits proliferation and DNA synthesis | Caco-2 cells | [79] |
| Radioimmunoassay | Decreased intracellular cAMP levels | |||
| Flow cytometry analysis | Influence on the tumor cell cycle: G2-M period shortened, cell cycle lengthened, and cell proliferation inhibited | U14 cells | [92] | |
| cis-DDP-induced | Potentiated the inactivating effect of cis-DDP in all phases of the cell cycle | NHIK 3025 cells | [82] | |
| Trypan-blue assay | Anticancer activity | HL-60, A549, PC3, Du145, LN-CaP, A172, U251, SKMEL28, and A375 cells | [93, 94] | |
| Flow cytometry analysis | Inhibition and induced-differentiation on human osteogenic sarcoma cells | Human osteogenic sarcoma cells | [95] | |
| MTT assay | Cytotoxic activity | HepG2 cells | [97] | |
| Spectrophotometer | Higher antioxidant capacity | |||
| NRU assay | Cytotoxic activity | Mac Coy cells | [96] | |
| MTT assay | Antiviral activity | EHV-1 | [98] | |
|
| ||||
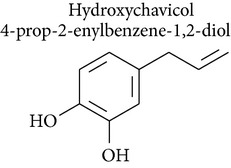
|
Trypan-blue assay |
Cytotoxic activity |
Rat hepatocytes | [54] |
| Waters chromatograph |
Decrease in cell viability, accompanied by losses of ATP, GSH; increase in GSSG, ROS, and MDA levels |
|||
|
| ||||
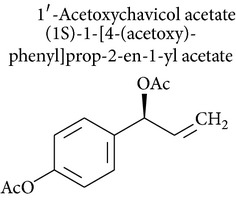
|
Indirect immunofluorescent method/EBV activation |
Inhibiting the generation of anions during tumor promotion |
Raji cells |
[100] |
| Trypan-blue exclusion assay | Cytotoxic activity | RPMI8226, U266, and IM-9 cells | [99] | |
| Flow cytometry | Induced caspases 3, 9, and 8 activities | RPMI8226 cells | ||
| Western blot analysis | TNF-α-induced apoptosis | |||
| ELISA | Downregulation of NF-κB activity | |||
| TNF-α-induced apoptosis | ||||
|
In vivo assay |
Anticancer effects with no toxic effects |
NOD/SCID mouse |
||
