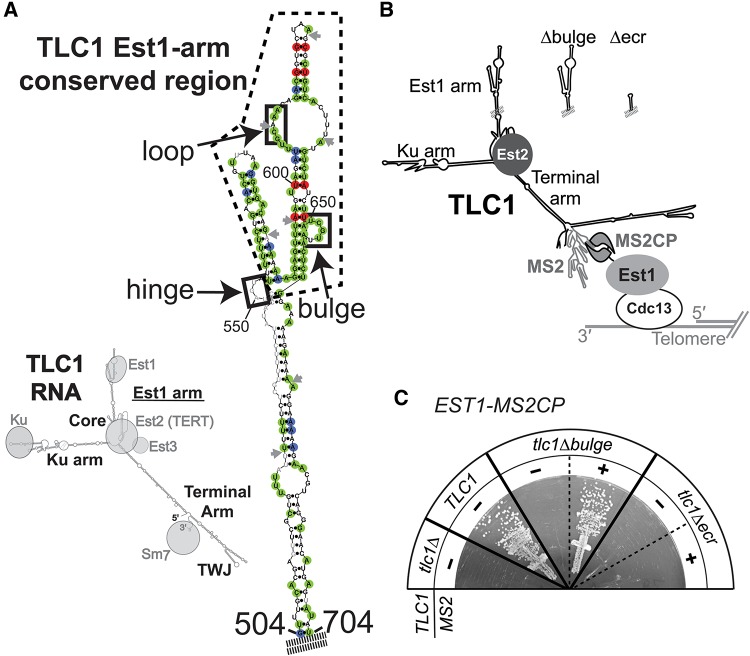
FIGURE 1.
The Est1-binding arm of TLC1 has a second essential function in telomere maintenance. (A) The Est1-arm conserved region of TLC1 telomerase RNA. (Left) Phylogenetically supported secondary structure for TLC1 (Zappulla and Cech 2004) bound to protein subunits. (Right) The phylogenetically supported secondary structure of the S. cerevisiae Est1-binding arm of TLC1, with nucleotides highlighted based on the sequence alignment of 36 telomerase RNAs from seven Saccharomyces species (see also Supplemental Fig. S1). Green = 100% conservation, red = covarying, blue = varying while maintaining base-pairing. Gray nucleotides, absent in one or more sequences. Gray arrows, locus of ≥1 nt insertion in one or more sequences. Dashed line indicates 108-nt Est1-arm conserved region (nucleotides 554–661). Solid black boxes indicate elements proposed to be required for Est1 association. (B) Schematic of MS2-tethered Est1 mediating telomerase RNP recruitment to the telomere. (C) MS2-tethering Est1 to tlc1Δbulge, but not tlc1Δecr, is sufficient for telomerase function. TLC1 alleles with or without MS2 hairpins were expressed in EST1-MS2CP cells. Streaks are shown at 125 generations of growth.