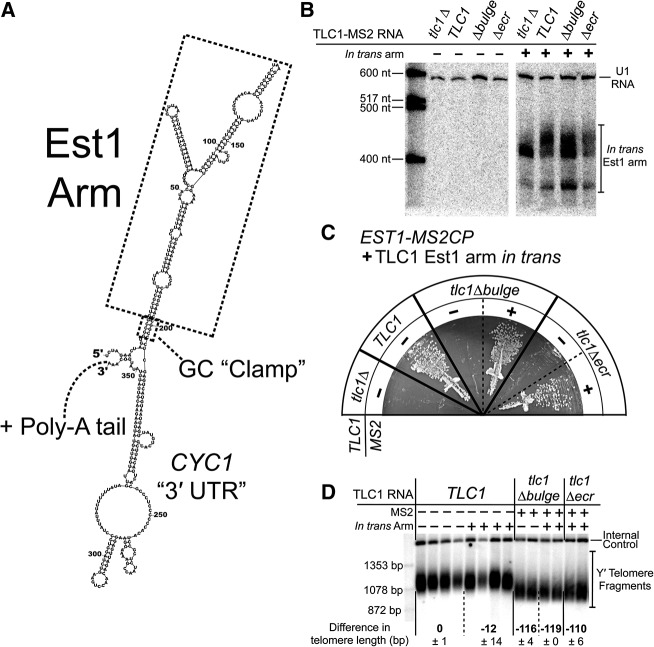
FIGURE 2.
Expression of the Est1 arm in trans restores telomerase activity to the condition where Est1 is MS2-tethered to tlc1Δecr. (A) Lowest energy Mfold secondary structure prediction for the in trans arm RNA transcript. The Est1 arm is predicted to fold as in TLC1. A GC “clamp” at the base of the Est1 arm helps to ensure proper folding. Upstream and downstream sequences are derived from the TEF2 promoter and CYC1 terminator, respectively. Like wild-type TLC1, the in trans RNA is a Pol II transcript, and is expected to be polyadenylated. (B) Northern blot probed for Est1-arm expression in Est1-MS2CP cells. The two Est1-arm bands correspond to predicted sizes for a nonpolyadenylated arm (∼389 nt; lower band) and a polyadenylated arm (∼400–450 nt; upper band). (C) TLC1 alleles with or without MS2 hairpins expressed in EST1-MS2CP cells along with the Est1 arm in trans. Streaks shown at 125 generations of growth. Presence of the in trans Est1 arm rescues cells with tlc1Δecr only when the TLC1 mutant is tethered to Est1 protein. (D) Telomere Southern blot for Est1-MS2CP cells with or without the in trans Est1 arm. Two or four independent transformants are shown for each condition after 250 generations of growth. Average changes in Y′ telomere length relative to TLC1 are indicated ± SD. Internal control = nontelomeric Xho I fragment from chromosome IV.