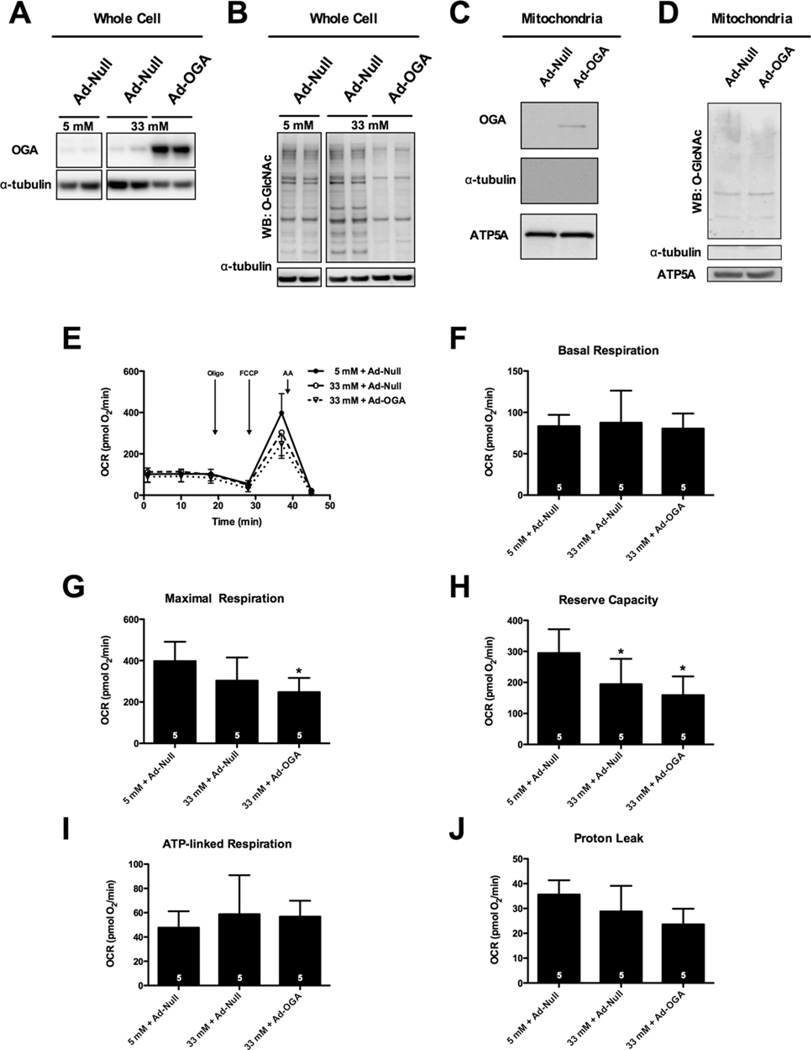
Figure 5. Overexpression of OGA does not rescue high-glucose-induced suppression of bioenergetic reserve.
NRCMs were transduced with virus to overexpress OGA prior to treatment with hyperglycaemia. Ad-Null was used as a vector control. (A) Immunoblot for whole-cell OGA protein expression following viral transduction. (B) Whole-cell protein O-GlcNAcylation levels following adenoviral transduction. (C) Immunoblot for mitochondrial OGA following adenoviral overexpression. (D) Immunoblot for mitochondrial protein O-GlcNAcylation following adenoviral overexpression of OGA. (E) Mitochondrial function assay following 48 h of hyperglycaemic treatment. From assay in (E) parameters of mitochondrial function were measured: (F) basal respiration, (G) maximal respiration, (H) reserve capacity, (I) ATP-linked respiration, and (J) proton leak. As indicated in bars, n = 5 independent experiments; *P < 0.05, compared with 5 mM glucose + Ad-Null.