Figure 4.
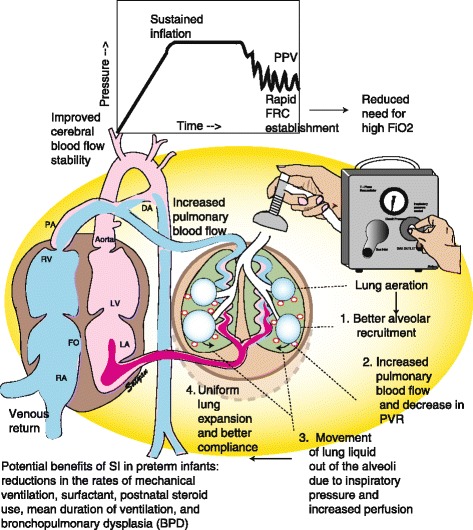
Sustained inflation (SI) in neonatal resuscitation. The fluid filled lung of a newborn infant potentially benefits from prolonged inspiratory time and pressure of SI to facilitate (1) alveolar recruitment, (2) increased pulmonary blood flow and decreased pulmonary vascular resistance, (3) movement of lung liquid out of the alveoli, and (4) uniform lung expansion and better compliance. Rapid establishment in FRC results in improved cerebral blood flow stability and reduced need for FiO2. DA ductus arteriosus, FiO2 fraction of inspired oxygen, FRC functional residual capacity, LA left atrium, LV left ventricle, PA pulmonary artery, PPV positive pressure ventilation, PVR pulmonary vascular resistance, RA right atrium, RV right ventricle. Copyright Satyan Lakshminrusimha.
