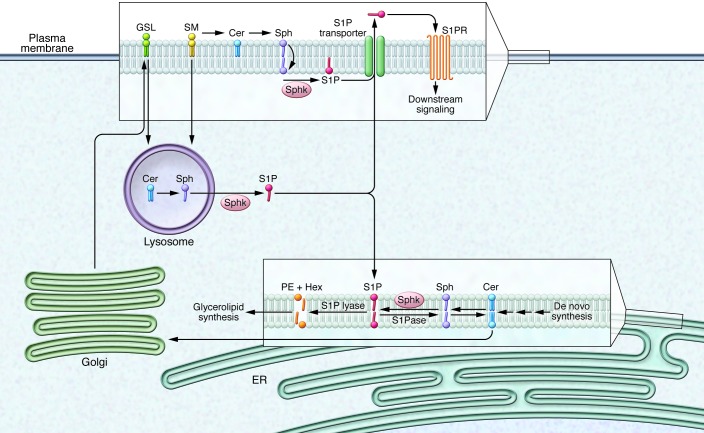
Figure 1. S1P synthesis, metabolism, and export.
Sphingomyelin (SM) and glycosphingolipids (GSL) are localized to plasma membrane microdomains. Degradation of plasma membrane sphingolipids into ceramide (Cer) and then ultimately to sphingosine (Sph) occurs in lysosomes and at the plasma membrane. Phosphorylation mediated by sphingosine kinases leads to the formation of S1P, which follows one of three pathways: (a) S1P is exported by transporters, such as SPNS2, where it can interact with its GPCRs (S1P1–S1P5) on the cell surface; (b) S1P is degraded by S1P lyase into hexadecenal (Hex) and phosphoethanolamine (PE), which are shunted into the glycerolipid biosynthetic pathway; or (c) S1P is dephosphorylated by S1P phosphatase for recycling of sphingosine into ceramide synthesis. S1PR, S1P receptor; S1Pase, S1P phosphatase.