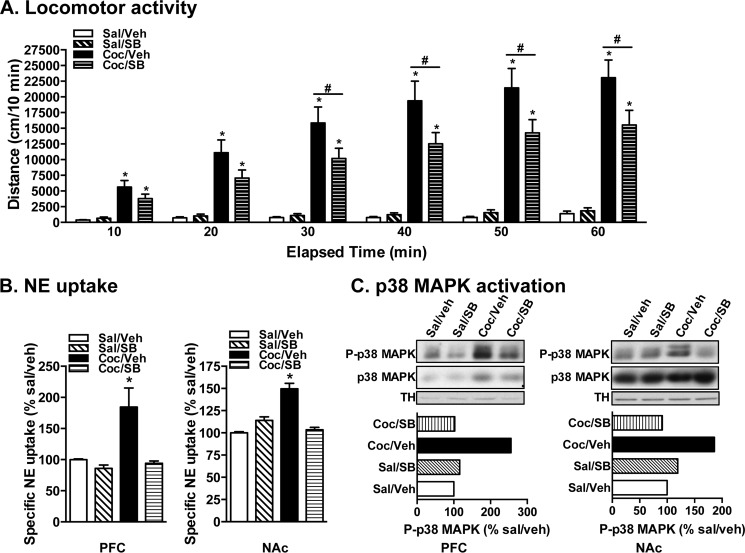
FIGURE 3.
In vivo p38 MAPK inhibition attenuates cocaine-induced locomotor sensitization, NET up-regulation, and p38 MAPK activation in mice. A, locomotor activity. Locomotor activity measured over a 1-h period on challenge day given as 10-min bin data. 50 μg/kg intraperitoneal SB203580 (SB) given prior to cocaine (Coc) challenge significantly blocked cocaine sensitization. * indicates significant changes in locomotor activity (*, p < 0.001 for drug; #, p < 0.001 for time; two-way analysis of variance; Bonferroni's test: F(4,192) = 1086 for drug, p = 0.0001; F(6,192) = 113.4 for time, p = 0.0001; F(16,192) = 32.61 for interaction, p = 0.0001). B, NE uptake. PFC and NAc synaptosomes were used for NE uptake assays as described under “Experimental Procedures.” NE uptake data derived from three separate experiments, each in triplicate, are given as mean ± S.E. (error bars). * indicates a significant change in NE transport (one-way analysis of variance; Dunnett's test: F(4,44) = 3.2 for PFC, p < 0.05; F(4,47) = 5.86 for NAc, p < 0.05). C, p38 MAPK activation. PFC and NAc synaptosomes were solubilized, and equal aliquots of synaptosome extracts were subjected to SDS-PAGE and sequential immunoblotting with phospho-p38 MAPK (p-p38MAPK), total p38 MAPK, or TH antibodies. Representative blots of phospho (P)-p38 MAPK, total (T) p38 MAPK, and TH from two independent experiments are shown. Bar graphs below the immunoblots show mean values of quantified phospho-p38 MAPK densities (normalized to TH input) from two experiments. Veh, vehicle; Sal, saline.