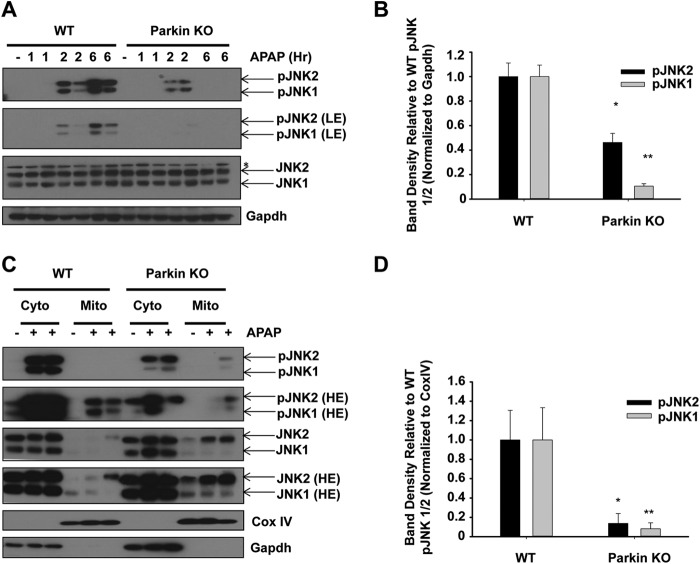
FIGURE 4.
Protection in Parkin KO mice may be due to decreased JNK activation. A, WT and Parkin KO mice were treated with 500 mg/kg APAP or saline control for 1, 2, or 6 h, and total liver lysates were analyzed by Western blot. Results from one representative mouse are shown for saline, and results from two representative mice are shown for APAP treatment. Gapdh was used as a loading control (LE, low exposure). B, densitometry quantification of pJNK. Data shown are means ± S.E. (n = 2 each for WT and Parkin KO saline, 3 each for WT and Parkin KO APAP-treated mice; *, p < 0.05 compared with WT APAP treatment at 6 h; **, p < 0.05 compared with WT APAP treatment at 24 h). Results were normalized to Gapdh. C, WT and Parkin KO mice were treated with 500 mg/kg APAP or saline control for 6 h, and cytosolic and mitochondrial fractions were analyzed by Western blot. CoxIV and Gapdh were used as loading controls for HM and cytosolic fractions, respectively (HE, high exposure). D, densitometry quantification of pJNK in the mitochondrial fraction. Data shown are means ± S.E. (n = 2 each for WT and Parkin KO saline treated mice, 3 each for WT and Parkin KO APAP-treated mice; *, p < 0.05 compared with WT APAP treatment at 6 h; **, p < 0.05 compared with WT APAP treatment at 24 h). Results were normalized to CoxIV.