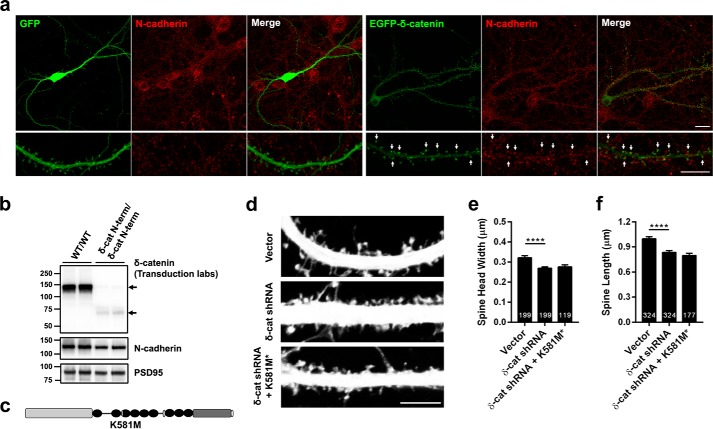
FIGURE 7.
The interaction of δ-catenin with N-cadherin is necessary for its ability to regulate spine architecture. a, confocal images of DIV 19–20, transfected at DIV 17, rat hippocampal neurons expressing EGFP or EGFP δ-catenin and immunostained for N-cadherin. N-cadherin is localized at spines and a significant amount of EGFP-δ-catenin and N-cadherin colocalize at spine heads (indicated by arrows). (Scale, top panel, 20 μm; bottom, 10 μm.) b, Western blot analysis of synaptosome from control and δ-catenin N-term mice with antibodies to δ-catenin and PSD-95. N-cadherin levels are significantly reduced in the δ-catenin N-term mouse synaptosomes (p = 0.023, Student's t test). c, schematic of construct used. d, representative images of dendrites from neurons expressing vector, shRNA, or shRNA + δ-catenin K518M* mutant that abolishes its interaction with N-cadherin. e, quantitation of spine head width, and f, spine length in neurons expressing vector, shRNA, or shRNA + K581M* (p values: *, <0.05; **, <0.005; ***, <0.0005, one-way ANOVA and Dunnett's multiple comparison test with single pooled variance; scale, 5 μm).