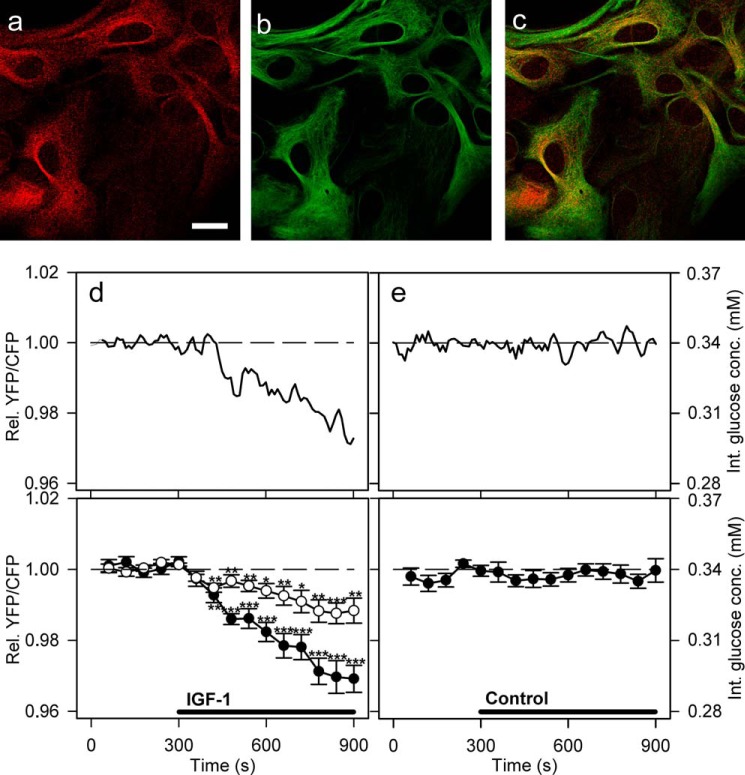
FIGURE 4.
Activation of IGF-1 receptors decreases glucose levels in cultured astrocytes. a–c, astrocytes immunolabeled with antibodies against IGF-1 receptors (a, red), astrocytic marker glial fibrillary acidic protein (b, green), and overlay of both signals (c). Scale bar, 20 μm. d and e, representative (upper panel) and mean (lower panel) time-dependent changes of the YFP/CFP (FRET) ratio signal upon IGF-1 or vehicle stimulation. IGF-1 stimulation (100 nm, black line) decreases the cytosolic glucose concentration in astrocytes (filled circles). Cells pretreated with 100 nm PPP (open circles), an IGF-1 receptor kinase inhibitor, were exposed to the same experimental conditions as nonpretreated cells. The mean change in the FRET ratio recorded on IGF-1 stimulation in PPP-pretreated cells was significantly lower (n = 20 cells) than in nonpretreated cells (n = 13 cells; p = 0.00017 at 600 s and p = 0.0014 at 900 s; Student's t test). e, cells superfused with vehicle extracellular solution (control) showed no significant change in the FRET ratio (n = 15 cells). Student's t test for paired data: *, p = 0.05; **, p = 0.01; ***, p = 0.001. conc., concentration; Int., internal; Rel., relative.