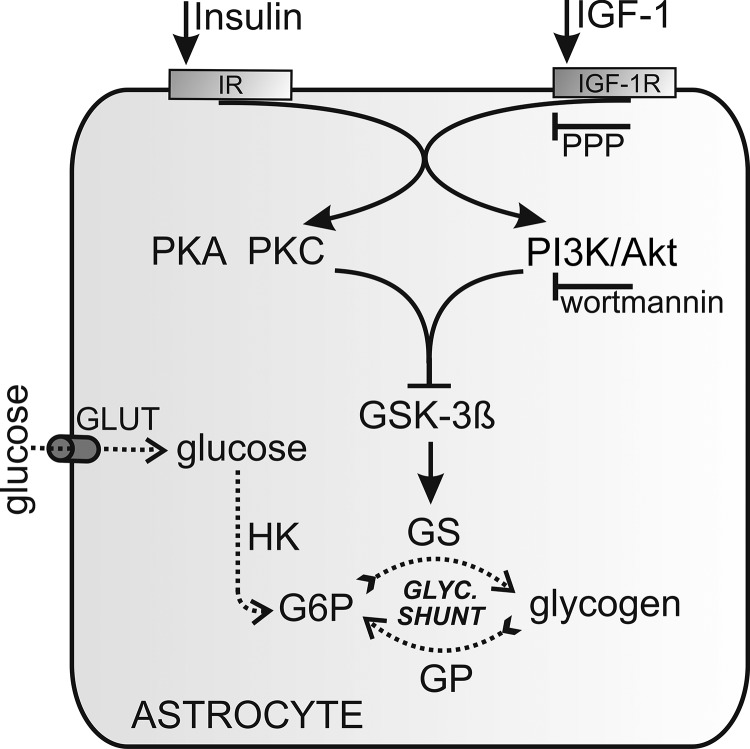
FIGURE 6.
Modulation of glycogen stores in astrocytes by insulin and IGF-1. After the binding of insulin or IGF-1 to their receptors, several mutual signaling pathways may be activated. The pathway leading to glycogen synthesis is the PI3K/Akt pathway. Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway inactivates GSK-3β. GSK-3β is also inactivated through the PKA and PKC pathways. Inactivated GSK-3β results in less phosphorylated and thus more active glycogen synthase (GS), which in turn depletes intracellular glucose 6-phosphate (G6P) and lowers the glucose concentration. GLUT1 and GLUT3 are major glucose transporters in astrocytes; GLUT4 is also present. Glucose is phosphorylated by hexokinase (HK) to produce glucose 6-phosphate, which in turn negatively regulates the activity of hexokinase. The effect of IGF-1 is inhibited by a selective IGF1R inhibitor, PPP, and the PI3K/Akt pathway is inhibited by wortmannin, a selective PI3K inhibitor.