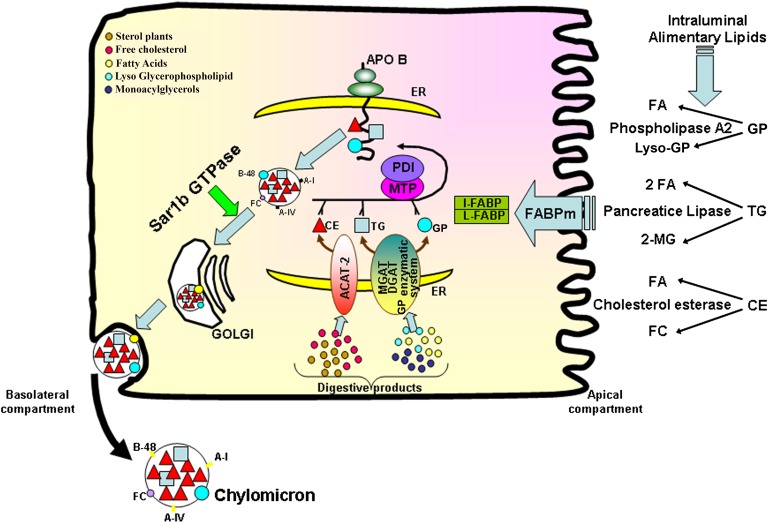
Fig. 1.
Schematic intracellular network required for lipid metabolism, Apo B biogenesis, and CM assembly in the enterocyte. Digestion takes place in the intestinal lumen where TGs, CEs, and GPs are hydrolyzed by pancreatic lipase, cholesterol esterase, and phospolipase A2, respectively. The lipolytic products (FA, 2-MG, FC, lyso-GP) are emulsified into mixed micelles by bile salts before their diffusion through the unstirred water layer. At the apical surface, they enter the enterocyte via passive diffusion when they are in high concentrations. However, protein transporters (e.g., FABPm) are required at weaker concentrations. Once inside the enterocyte, the lipolytic products are bound to cytoplasmic FABPs (I- and L-FABP) in order to migrate to the ER where they are reesterified by various enzymes: monoacylglycerol acyltransferase (MGAT) and diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT) for the conversion of 2-MG to TG, ACAT-2 for the esterification of FC into CE, and an enzymatic system (glycerophosphate acyltransferase, phosphatidate phosphodiesterase, lyso-PC acyltransferase) for the production of GP. The synthesis of Apo B-48 and its interaction with MTP, a heterodimeric complex with the chaperone protein, protein disulfide isomerase (PDI), through the NH2-terminal domain, is essential for preCM assembly. This packaging process starts when the growing Apo B-48 polypeptide is cotranslationally lipidated by MTP in the lumen of the ER: the association of Apo B-48 with lipids is required not only to ensure proper initiation of folding, but also to prevent its destruction by the proteosomal degradation pathway. The formation of preCM transport vesicles is critical for the transport of the nascent lipoproteins to the Golgi, a process mediated by Sar1b GTPase. The maturation of preCMs is completed in the Golgi by addition of lipids and glycosylation of Apos, yielding a mature CM particle characterized by TG and CE in its core and FC, GP, and Apo B on its surface. Finally, CMs are released by the enterocyte into the intestinal lymph through exocytosis. MG, monoacylglycerol; FC, free cholesterol; I-FABP, intestinal-FABP; L-FABP, liver-FABP; PC, phosphatidylcholine.