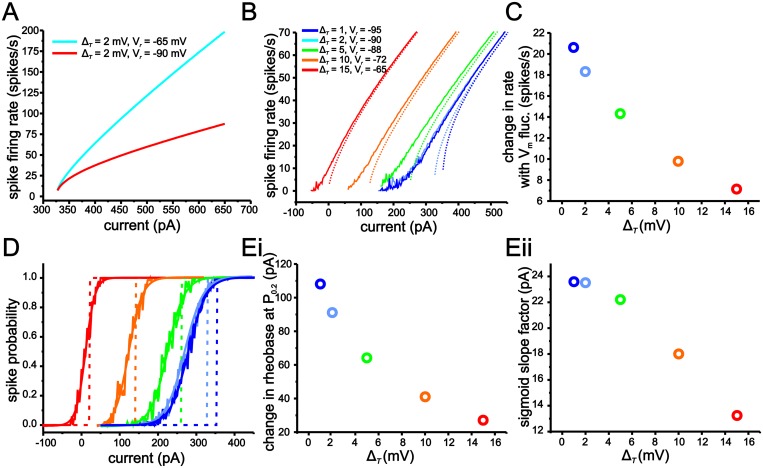
Fig 5. Reducing ΔT in the eLIF model gradually increases modulation of input-output responses by membrane voltage fluctuations.
(A) eLIF model f-I curve gain is reduced with more a negative Vr value. (B) Comparison of f-I curves for different ΔT values with (solid lines) and without (dash lines) membrane voltage fluctuations. Note, more negative Vr values were used to maintain the same gain with smaller ΔT values. (C) Changes in the initial firing rate of f-I curves induced by membrane voltage fluctuations for the eLIF model using ΔT values. (D) Comparison of spike-probability curves for different ΔT values with (solid lines) and without (dash lines) membrane voltage fluctuations. (E) Plots of changes in rheobase (i) and sigmoid slope factor (ii) on spike-probability measures associated with the introduction of membrane voltage fluctuations for eLIF models using different ΔT values.