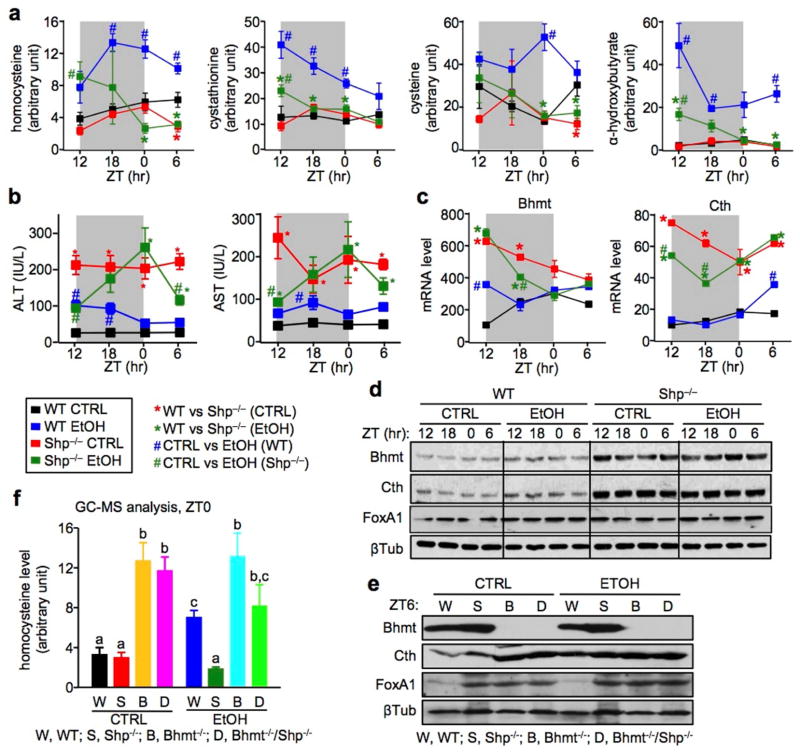
Figure 4. Shp−/− mice are resistant to alcohol-induced hyperhomocysteinemia.
a, GC/MS analysis of Hcy metabolites. Sera were collected from WT CTRL (black), WT EtOH (blue), Shp−/− CTRL (red), and Shp−/− EtOH (dark green) mice over a 12h/12h light/dark cycle using the NIAAA-binge model. Five individual mice were analyzed in each group. Data are shown in mean ± SEM (n=5). *P < 0.01, Shp−/− vs WT; #P < 0.01, EtOH vs CTRL. ZT, Zeitgeber time.
b, Serum ALT and AST levels in WT CTRL (black), WT EtOH (blue), Shp−/− CTRL (red), and Shp−/− EtOH (dark green) mice over a 12h/12h light/dark cycle using the NIAAA-binge model. *P < 0.01, Shp−/− vs WT; #P < 0.01, EtOH vs CTRL. ZT, Zeitgeber time.
c, qPCR of hepatic Bhmt and Cth mRNA in WT CTRL (black), WT EtOH (blue), Shp−/− CTRL (red), and Shp−/− EtOH (dark green) mice over a 12h/12h light/dark cycle using the NIAAA-binge model. *P < 0.01, Shp−/− vs WT; #P < 0.01, EtOH vs CTRL. ZT, Zeitgeber time.
d, Western blot of hepatic Bhmt, Cth, and FoxA1 protein expression in WT CTRL, WT EtOH, Shp−/− CTRL, and Shp−/− EtOH mice over a 12h/12h light/dark cycle using the NIAAA-binge model. β-Tublin (βTub), loading control.
e, Western blot of hepatic Bhmt, Cth, and FoxA1 protein expression at ZT0 in WT (W), Shp−/− (S), Bhmt−/− (B), and Bhmt−/−Shp−/− (D) mice using the NIAAA-binge model. β-Tublin (βTub), loading control.
f, GC/MS analysis of serum homocysteine levels at ZT0 in WT (W), Shp−/− (S), Bhmt−/− (B), and Bhmt−/−Shp−/− (D) mice using the NIAAA-binge model. Data are shown in mean ± SEM (n =5). Different characters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05).