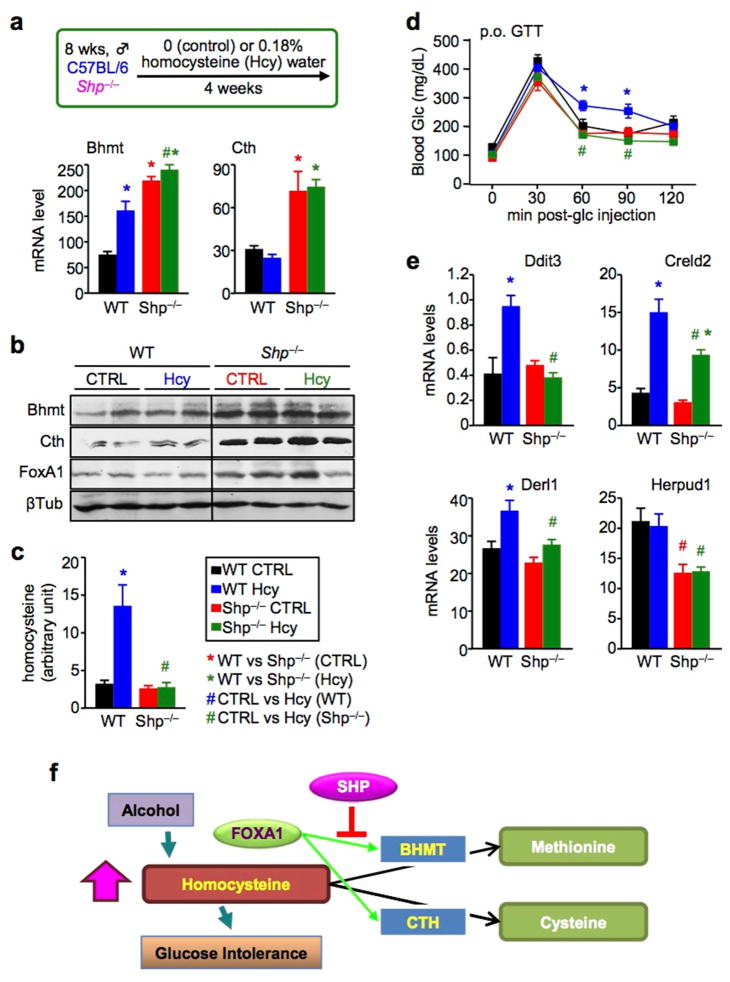
Figure 6. Homocysteine-induced glucose intolerance is diminished in Shp−/− mice.
a, (upper) Mouse model of chronic HHcy. WT and Shp−/− mice fed with a chow diet were supplied with drinking water containing 0.18% of DL-Hcy for four weeks. (lower) qPCR of hepatic Bhmt and Cth mRNA in WT CTRL (black), WT Hcy (blue), Shp−/− CTRL (red), and Shp−/− Hcy (dark green) mice. Data are shown in mean ± SEM (n = 5). *P < 0.01 vs WT CTRL; #P < 0.01, Shp−/− Hcy vs WT Hcy.
b, Western blot of hepatic Bhmt, Cth, and FoxA1 protein expression in WT CTRL, WT Hcy, Shp−/− CTRL and Shp−/− Hcy mice. β-Tublin (βTub), loading control.
c, Serum Hcy levels in WT CTRL (black), WT Hcy (blue), Shp−/− CTRL (red), and Shp−/− Hcy (dark green) mice. Data are shown in mean ± SEM (n = 5). *P < 0.01 vs WT CTRL; #P < 0.01, Shp−/− Hcy vs WT Hcy.
d, Oral glucose tolerance test in WT CTRL (black), WT Hcy (blue), Shp−/− CTRL (red), and Shp−/− Hcy (dark green) mice. Data are shown in mean ± SEM (n = 5). *P < 0.01 WT Hcy vs WT CTRL; #P < 0.01, Shp−/− Hcy vs WT Hcy.
e, qPCR of mRNA for ER-stress target genes in the liver of WT CTRL (black), WT Hcy (blue), Shp−/− CTRL (red), and Shp−/− Hcy (dark green) mice. Data are shown in mean ± SEM (n = 5). *P < 0.01 vs WT CTRL; #P < 0.01, Shp−/− Hcy vs WT Hcy.
f, Schematics of findings in the present study. SHP is a new modulator of Hcy metabolism by suppressing FoxA1-induced Bhmt and Cth expression. Shp-deficiency results in upregulation of Bhmt and Cth, which in turn facilitates Hcy catabolism, diminishes alcohol-induced HHcy, and prevents HHcy-induced glucose intolerance.