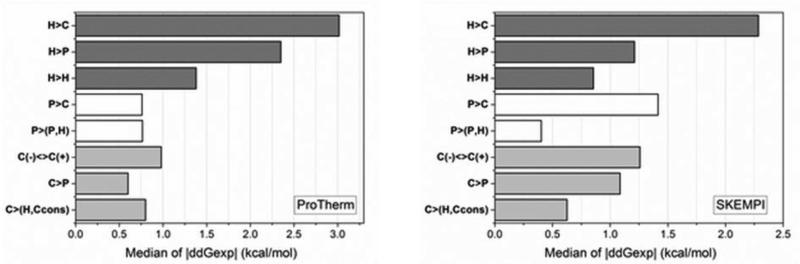
Fig. 7.
The median of experimental folding and binding free energy absolute change caused by mutations taken from ProTherm and Skempi databases and grouped according to largest effect and the rest of cases. Single arrow represents substitution for one type residue to another, as for example H>C is mutation from wild type hydrophobic to charged amino acid in the mutant. Charged residues (C): R, K, D, and E; polar residues (P): S, T, N, and Q; hydrophobic residues (H): A, V, I, and L. R and K are positively charged residues noted as C(+); while D and E – negatively charged residues noted as C(-). During C<>Ccons amino acid substitutions the charge of the residue conserves, that includes C(+)>C(+) and C(-)>C(-) groups of mutations.