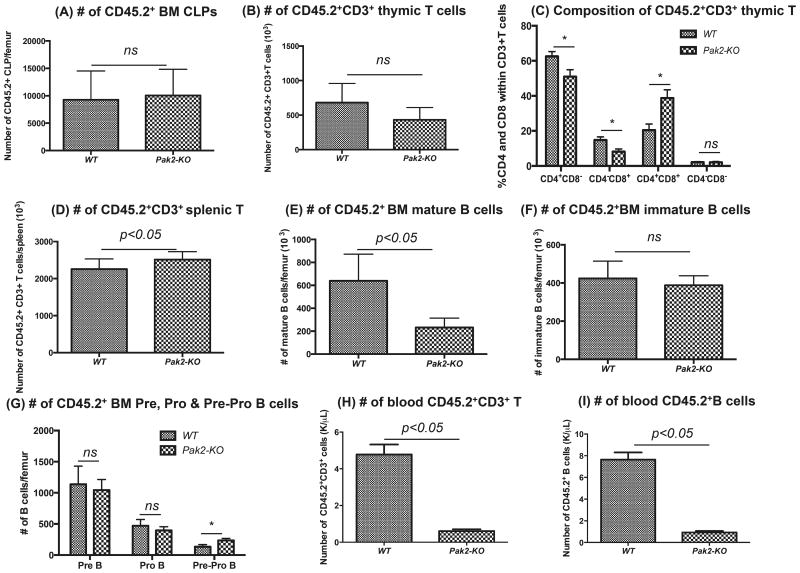
Figure 7. Loss of Pak2 leads to deficient lymphopoiesis.
A) Absolute number of CD45.2+ common lymphoid progenitors (CLPs: Lin−IL7Ra+c-KitlowSca1low), (B) number of CD45.2+CD3+ T cells in thymus, (C) percentage of CD4+CD8+, CD4+CD8−, CD4−CD8+ and CD4−CD8− cells within the CD45.2+CD3+ thymic T cell population, (D) number of CD45.2+CD3+ T cells in spleen, (E) numbers of CD45.2+ BM mature B cells (B220+lgM+lgD+), (F) numbers of CD45.2+ BM immature B cells (B220+lgM+lgD−), (G) numbers of CD45.2+ BM Pre B (B220+lgM−lgD−CD43−CD24high), Pro B (B220+lgM−lgD−CD43+CD24med) and Pre-Pro B cells (B220+lgM−lgD−CD43+CD24−), (H) number of peripheral blood CD45.2+CD3+ T cells and (I) number of peripheral blood CD45.2+B220+ B cells was determined by flow cytometry. Absolute number of each cell population was obtained by multiplying the percentage with cellularity of thymus or spleen or WBC count. N=4-6 mice/group. Student t test, * indicates p<0.05 between Pak2-KO and WT. Representative data from 2-3 experiments.