Figure 1.
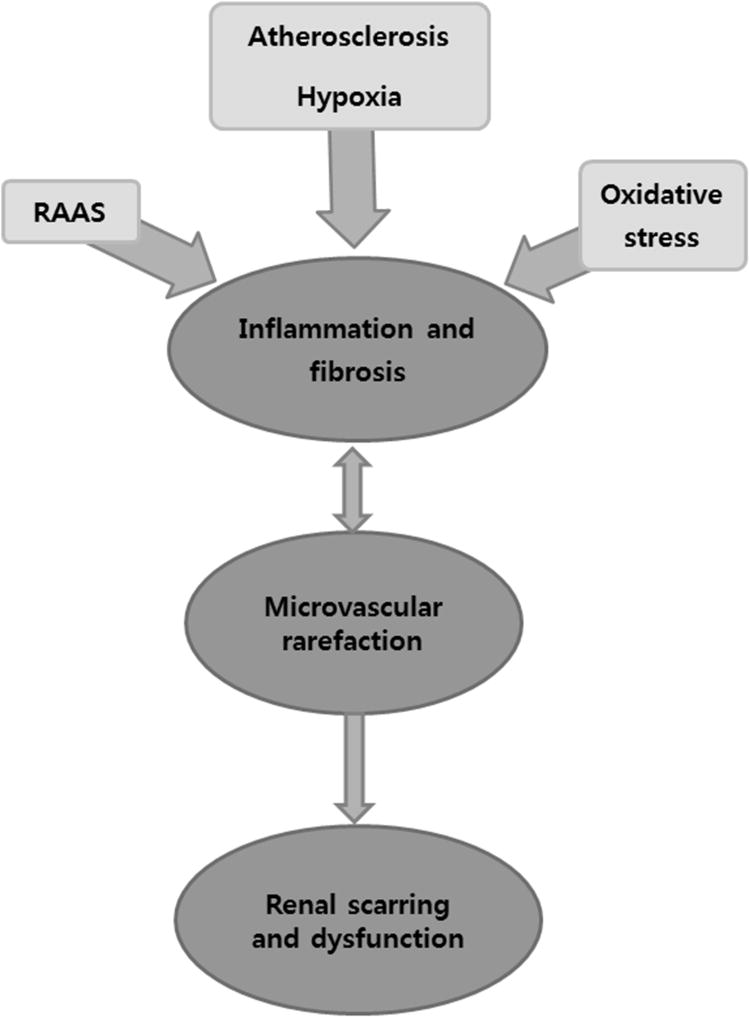
Schematic of interactive mechanisms responsible for kidney injury in atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis (ARAS). A critical renovascular occlusion activates the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), elicits hypoxia, and increases oxidative stress. Together with atherosclerosis this process induces parenchymal inflammation, fibrosis, microvascular loss, and kidney dysfunction.
