Figure 3. Principle of the K-means Algorithm Used in Single-Particle EM Structure Determination Protocols.
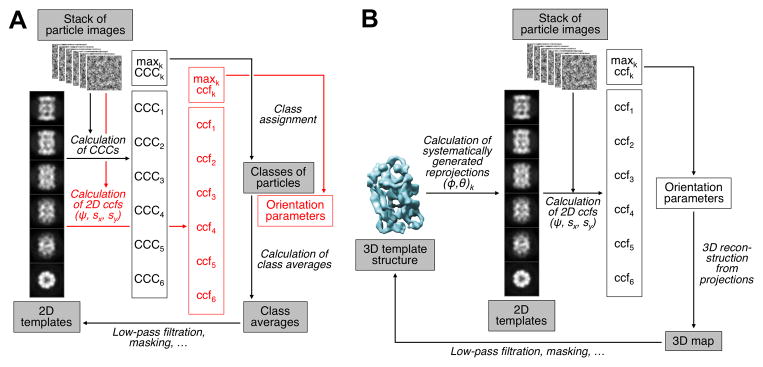
(A) In the basic K-means algorithm, the particle images are compared with a set of class averages using a correlation measure that yields the class assignment. Based on the updated class assignments, new class averages are then calculated. Simply by adding 2D alignment of the images to the templates using a correlation function, the algorithm is converted to Multi-Reference Alignment (MRA) (indicated by text in red font).
(B) Principle of the projection matching technique used for 3D single-particle EM structure refinement. The best match of an image to a template yields the Euler angles that were used to generate the template, while a 2D alignment step yields the third, in-plane Euler angle and the two in-plane translations, the total of five orientation parameters required for 3D reconstruction step.
