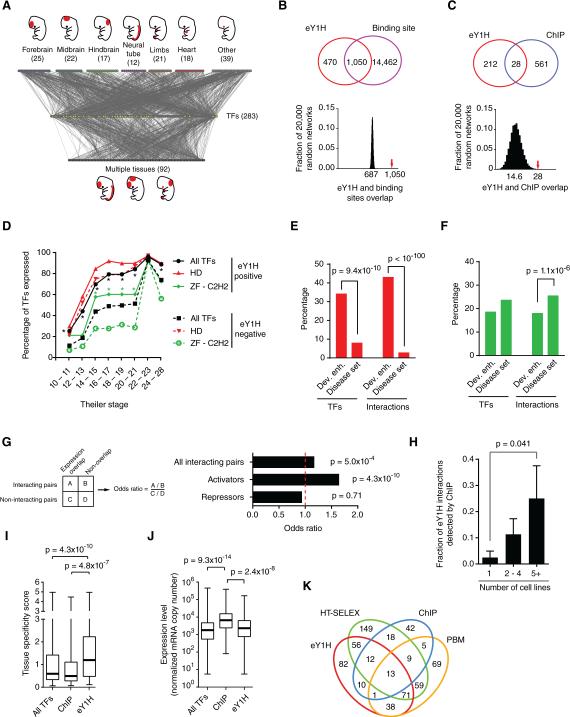
Figure 2. A Human Gene-Centered TF-Enhancer Interaction Network.
(A) The TF-enhancer interaction network comprises 2,230 interactions between 246 human developmental enhancers and 283 TFs. Enhancers that are active in a single tissue at day E11.5 (top nodes) or multiple tissues (bottom nodes) are connected to the TFs (middle yellow nodes) with which they interact.
(B, C) eY1H interactions significantly overlap with the occurrence of known TF binding sites (B) and ChIP peaks (C). The Venn diagrams on the left illustrate the number of overlapping interactions. The eY1H network was randomized 20,000 times by edge switching (Martinez et al., 2008) and the overlap in each randomized network was calculated (right panel). The numbers under the histogram peaks indicate the average overlap in the randomized networks. The red arrows indicate the observed overlap in the real network.
(D) Timing of expression during mouse development for homeodomain (HD) and ZF-C2H2 families. The fraction of TFs whose expression was detected at a particular Theiler Stage during development. *p < 0.01 by Fisher's exact test.
(E, F) Percentage of TFs or interactions involving homeodomains (E) or ZF-C2H2 TFs (F) for two datasets. Statistical significance determined by proportion comparison test.
(G) Overlap between enhancer activity and TF expression pattern. The fraction of TF-enhancer pairs that overlap in expression was compared between interacting and non-interacting pairs. The same analysis was performed for known activators and repressors. Statistical significance was determined using Fisher's exact test.
(H) The fraction of eY1H interactions that were also detected by ChIP were partitioned based on the number of cell lines in which a particular TF was tested by ChIP. p = 0.041 by Mann-Whitney's U test.
(I) Tissue specificity score for TFs detected by eY1H (n = 266), ChIP (n = 96) or all TFs present in the eY1H array (n = 896), based on their expression levels across 34 tissues (Ravasi et al., 2010). This score quantifies the departure of the observed TF expression pattern from the null distribution of uniform expression across all tissues, using relative entropy. Each box spans from the first to the third quartile, the horizontal lines inside the boxes indicate the median value and the whiskers indicate minimum and maximum values. Statistical significance determined by Mann-Whitney's U tests.
(J) The maximum expression level across 34 tissues were obtained from (Ravasi et al., 2010) for each TF detected eY1H (n = 266), ChIP (n = 96) or all TFs present in the eY1H array (n = 896) are plotted. Each box spans from the first to the third quartile, the horizontal lines inside the boxes indicate the median value and the whiskers indicate minimum and maximum values. Statistical significance determined by Mann-Whitney's U tests.
(K) Venn diagram depicting the overlap between TFs detected by eY1H and those detected by high-throughput SELEX (HT-SELEX), ChIP-seq and protein binding microarrays (PMBs).