Fig 1.
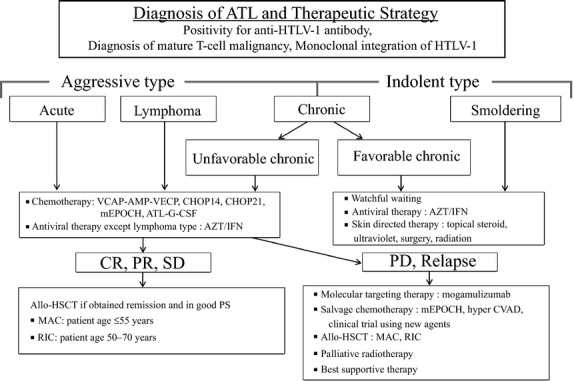
Treatment algorithm for adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma (ATL) patients. ATL diagnosis is based on anti-HTLV-1 antibody positivity in the serum, the presence of mature T-cell malignancy, and the Southern blot detection of monoclonal integration of HTLV-1 proviral DNA in the tumor cells. ATL treatment is usually determined according to the clinical subtypes and prognostic factors. The presence of an aggressive-type ATL (acute, lymphoma and chronic types with poor prognostic factors) or indolent-type ATL (chronic and smoldering types without poor prognostic factors) is critical when making treatment decisions. Patients with an aggressive-type (acute, lymphoma and unfavorable chronic type) generally receive immediate combination chemotherapy or antiviral therapy with zidovudine and interferon-α (AZT/IFN), except for those with the lymphoma type. The international consensus meeting primarily recommends the VCAP-AMP-VECP regimen. Other therapeutic regimens include CHOP14, CHOP21, mEPOCH and ATL-G-CSF. The patients undergo further treatment with allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, which is particularly effective in young patients with good performance statuses, and those who have achieved remission before transplantation. In Japan, patients with an indolent-type ATL without any skin lesions are usually followed up under a watchful waiting policy until the disease transforms to an aggressive type. Antiviral therapy is frequently performed for favorable chronic and smoldering ATL patients in non-Japanese nations, and skin directed therapy is applied for smoldering ATL with skin manifestations. allo-HSCT, allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; ATL-G-CSF, combination chemotherapy consisting of vincristine, vindesine, doxorubicin, mitoxantrone, cyclophosphamide, etoposide, ranimustine, and prednisone with granulocyte-colony stimulating factor support; AZT/IFN, zidovudine and interferon-α; CHOP, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone (CHOP14 is performed every 2 weeks and CHOP21 is performed every 3 weeks); CR, complete remission; hyper CVAD, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone; MAC, myeloablative conditioning; mEPOCH, etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin (EPOCH) with modifications; PD, progressive disease; PR, partial remission; PS, performance status; RIC, reduced intensity conditioning; SD, stable disease; VCAP-AMP-VECP, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin and prednisone (VCAP)-doxorubicin, ranimustine and prednisone (AMP)-vindesine, etoposide, carboplatin and prednisone (VECP).
