Fig 4.
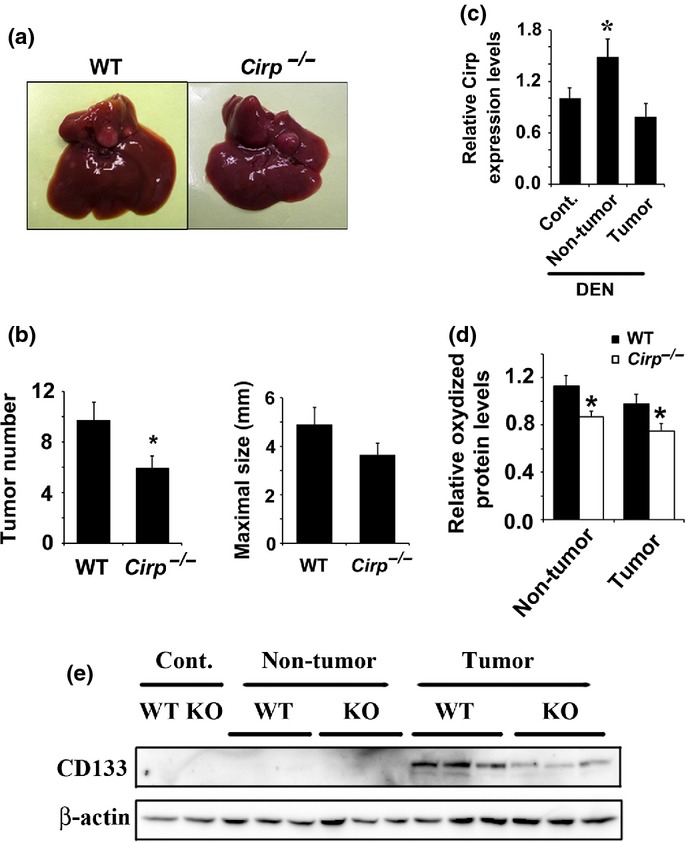
Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (Cirp) deficiency inhibited DEN-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. WT and Cirp−/− mice were injected with diethylnitrosamine (DEN) injection (25 mg/kg) and killed 8 months later. (a) Representative livers of WT and Cirp−/− mice. (b) Tumor number (>0.5 mm) and tumor size in livers of WT (n = 8) and Cirp−/− mice (n = 8). Data are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05 compared with WT mice. (c) Liver RNA was extracted from non-treated livers (Cont.), non-tumor tissues, and tumors. Relative mRNA amounts of Cirp were determined by real-time quantitative PCR and normalized to the amount of actin mRNA. The amount of mRNA in untreated liver was given an arbitrary value of 1.0. Results are means ± SEM (n = 5). *P < 0.05 compared with non-treated liver (Cont.). (d) Lysates of non-tumor liver tissue from DEN-injected mice were extracted, assessed by immunoblotting, and quantified using image analysis software. The amount of protein oxidation in untreated liver was given an arbitrary value of 1.0. Results are means ± SEM (n = 4). *P < 0.05 versus WT mice. (e) Lysates of non-treated liver (Cont.), tumor, and non-cancerous liver tissue were assessed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.
