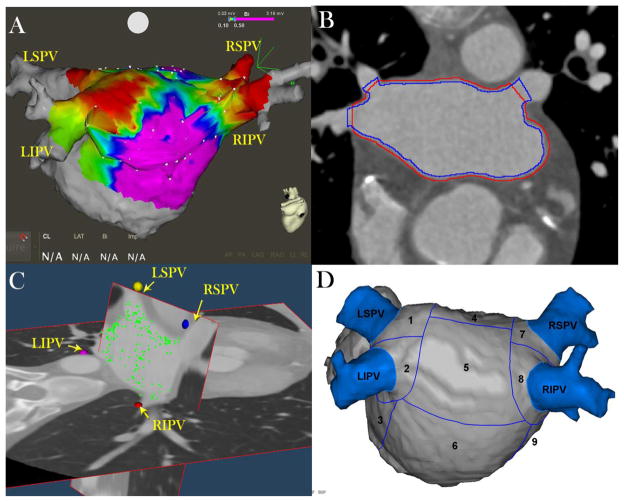
Figure 1. Image and Electrogram analysis Methodology.
Panel A: EAM points (white points) obtained invasively during sinus rhythm and merged with the left atrial (LA) endocardial shell obtained from the CE-MDCT image prior to the procedure. Regions with bipolar voltage <0.1 mV are highlighted in red and healthy regions with voltage >0.5 mV are highlighted in purple.
Panel B: Manually drawn endo- (blue line) and epicardial (red line) contours on CE-MDCT axial planes. The lines are drawn to cross each other at the pulmonary vein ostia to exclude the blood pool intensities from analysis.
Panel C: EAM points (green dots) are registered to the LA wall on 3D CE-MDCT images. The posterior wall has been hidden to allow the visualization of the PV ostia and the roof; therefore, in this image the posterior wall points are not visualized next to the wall.
Panel D: Summary of 13 left atrial segments in the posterior wall and the antrum of PVs.
LIPV = left interior pulmonary vein; LSPV = left superior pulmonary vein; RIPV = right inferior pulmonary vein; RSPV = right superior pulmonary vein; 1=LSPV antrum; 2=LIPV antrum; 3= mitral isthmus region; 4= upper posterior region; 5= middle posterior region; 6= lower posterior region; 7=RSPV antrum;8=RIPV antrum;9= septal region.