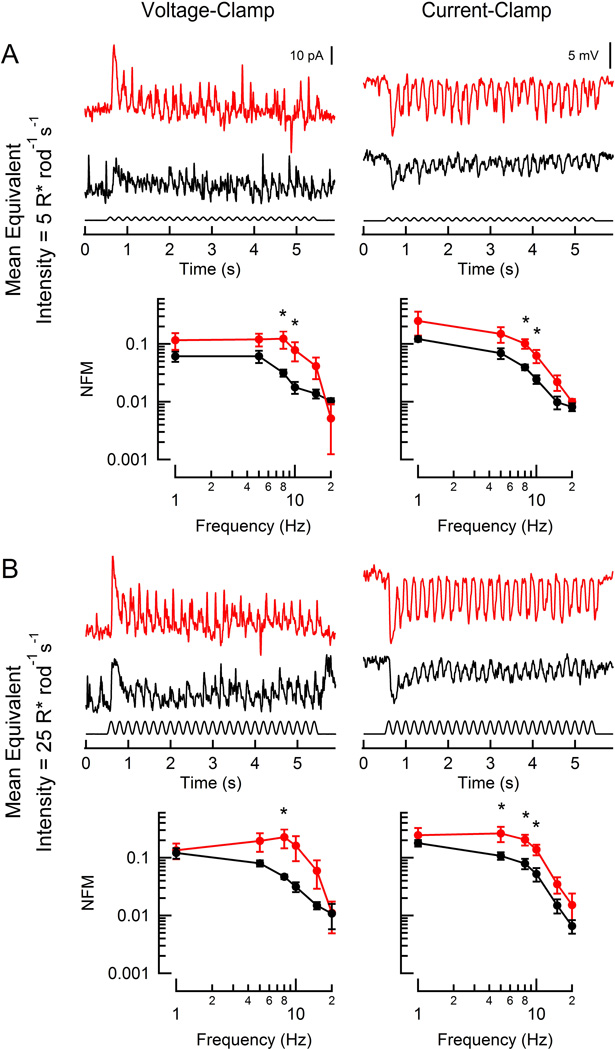
Figure 3. Responses of rod-driven HBCs to flicker.
Representative light-evoked current (left) and voltage (right) responses from two hyperpolarizing bipolar cells (red: RGS9-ox background; black: WT) to flicker (100% contrast; 5 Hz). WT and RGS9-ox slices were stimulated at intensities generating equivalent rod suppression (A: 5 and 10 R* rod−1 s−1; B: 25 and 50 R* rod−1 s−1). Population average magnitude spectra are plotted below each sample trace for each condition. Each data point reflects between 2 and 7 determinations from a total of 8 RGS9-ox and 6 WT HBCs. A statistically significant difference was observed at 5, 8, and 10 Hz (A, left: p = 0.034 and 0.031; A, right: p = 0.017 and 0.039; B, left: p = 0.035; B, right: p = 0.042, 0.013, and 0.017). Error bars represent SEM. NFM: normalized fundamental magnitude. *p < 0.05