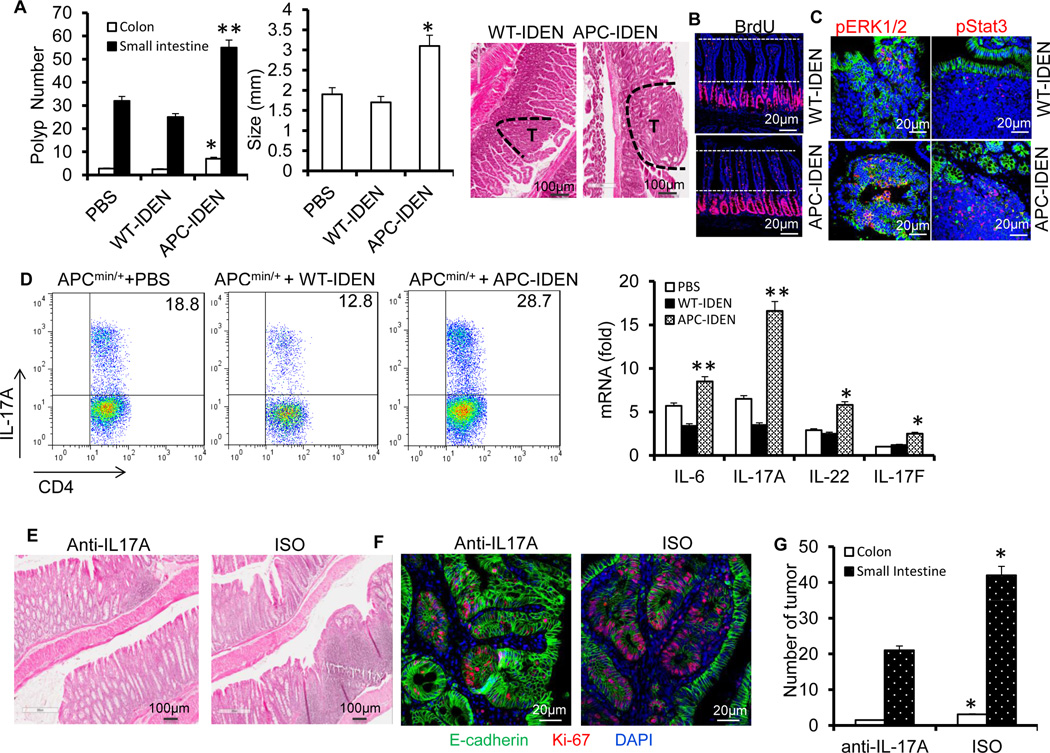
Figure 5. APC-IDENs promote tumor growth by inducing CCR6+CD4+Th17+ cells.
(A–C) APCmin/+ mice at six weeks of age were gavaged with IDENs once every three days for eight weeks. (A) Number and size of tumors and H&E-stained sections from 3-month-old APCMin/+ mice. (B) Mice were injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) with 50mg/kg of 5’-bromo-2’-deoxyuridine (BrdU) in PBS 24 h before small intestine harvest. BrdU antibody–stained small intestine sections. (C) A sectioned tumor was stained with anti-phospho-ERK antibody (red) or phospho-STAT3 (red) and E-cadherin (green). The data (A) represent means ± SEMs (n = 8). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (Student’s t-test).
(D) FACS analysis of IL-17A+ on CCR6+CD4+ T cells and real-time PCR for cytokine mRNAs in LPL CCR6+CD4+ T cells. The data represent means ± SEMs (n = 5). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (Student’s t-test).
(E–G) APCmin/+ mice gavaged with IDENs were treated with an anti-IL17A antibody or isotype. Representative photomicrographs of HE-stained colon sections (E), immunofluorescent staining of colon sections with anti-E-cadherin and Ki67 (F), and number of tumors (G).