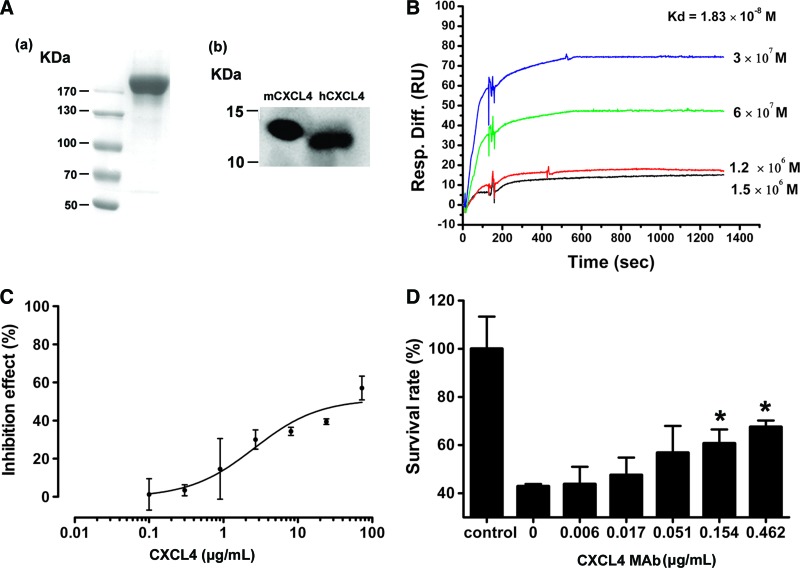
FIG. 4.
Characterization of CXCL4 MAb. (A) Purified CXCL4 MAb was analyzed by SDS/PAGE (a) and Western blot for reactivity with both rmCXCL4 (left) and rhCXCL4 (right) (b), respectively. 16D6-3 recognized CXCL4 with the molecular weight between 10 and 15 KDa. (B) Affinity measurement of CXCL4 MAb using Biacore. The response signals were obtained during the injection of gradient concentrations of rhCXCL4 (3×10−7 to 2×10−6 M, plus zero concentration) through flow cells immobilized with CXCL4 MAb. The kinetic profiles are shown. Association rates (kon) and dissociation rates (koff) are calculated using the one-to-one Langmuir binding model. The equilibrium dissociation constant (Kd) is derived as the kon/koff ratio. (C) rhCXCL4 inhibited growth of ACHN cells. (D) CXCL4 MAb neutralized effect of CXCL4 in the culture of ACHN cells. ACHN cells were cultured with rhCXCL4 at its IC50 (72.6 μg/mL). CXCL4 MAb inhibited the growth arrest of rhCXCL4 on ACHN in a dose-dependent manner. Data are presented as the mean±SD. **p<0.01 versus CXCL4 MAb of 0. Control refers to ACHN cells without treatment of rhCXCL4 and CXCL4 MAbs.